Kubernetes Ingress Concepts: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=Ingress Controller= | =Ingress Controller= | ||
The ingress controller is the process - most likely running as a pod or pods inside the Kubernetes cluster itself - that accepts the HTTP connections, distributes traffic, terminates SSL connections, etc. Some Kubernetes distributions provide an ingress controller as an "add-on". For example, minikube | The ingress controller is the process - most likely running as a pod or pods inside the Kubernetes cluster itself - that accepts the HTTP connections, distributes traffic, terminates SSL connections, etc. Some Kubernetes distributions provide an ingress controller as an "add-on". For example, minikube has a <code>minikube addons enable ingress</code> command. If the ingress controller is not provided as add-on, it can be installed. There is a default "ingress-nginx" ingress controller that can be installed in any Kubernetes instance. More details: {{Internal|ingress-nginx|ingress-nginx}} | ||
The ingress controller deploys as part of its installation a layer 4 service of its own, most likely a [[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#LoadBalancer_Service|LoadBalancer]]. As such, the ingress controller pod(s) is exposed to external requests via its own [[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#LoadBalancer_Service|LoadBalancer]]/[[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#NodePort_Service|NodePort]]/[[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#Service_.28ClusterIP_Service.29|ClusterIP]] service. | The ingress controller deploys as part of its installation a layer 4 service of its own, most likely a [[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#LoadBalancer_Service|LoadBalancer]]. As such, the ingress controller pod(s) is exposed to external requests via its own [[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#LoadBalancer_Service|LoadBalancer]]/[[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#NodePort_Service|NodePort]]/[[Kubernetes_Service_Concepts#Service_.28ClusterIP_Service.29|ClusterIP]] service. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
serviceName: b | serviceName: b | ||
servicePort: 80 | servicePort: 80 | ||
defaultBackend: | |||
service: | |||
name: c | |||
port: | |||
number: 81 | |||
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress | # This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress | ||
tls: | tls: | ||
| Line 80: | Line 85: | ||
The ingress must be deployed in the same namespace as the services it serves. | The ingress must be deployed in the same namespace as the services it serves. | ||
Upon deployment, the hosts served by an ingress, as well as its public address and port can be displayed with | Upon deployment, the hosts served by an ingress, as well as its public address and port can be displayed with the <code>kubectl get ingress</code> command. In the example below, the ingress and the ingress controller have been deployed locally on Docker Desktop Kubernetes, hence the "localhost": | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang='text'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='text'> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 96: | ||
==TLS Support== | ==TLS Support== | ||
<font color= | <font color=darkkhaki>TODO Kubernetes in Action Section 5.4.4.</font> | ||
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided: | If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided: | ||
| Line 105: | Line 110: | ||
tls.key: <base64 encoded key> | tls.key: <base64 encoded key> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
= | |||
{{ | ==Rewriting Paths== | ||
{{External|https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/main/docs/examples/rewrite/README.md}} | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='yaml'> | |||
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 | |||
kind: Ingress | |||
metadata: | |||
name: test | |||
annotations: | |||
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx | |||
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2 | |||
spec: | |||
rules: | |||
- host: somehost.example.com | |||
http: | |||
paths: | |||
- path: /prod(/|$)(.*) | |||
pathType: Prefix | |||
backend: | |||
service: | |||
name: service-prod | |||
port: | |||
number: 8080 | |||
- path: /stage(/|$)(.*) | |||
pathType: Prefix | |||
backend: | |||
service: | |||
name: service-stage | |||
port: | |||
number: 8080 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Different Ingresses with Different Path for the Same Host== | |||
<font color=darkkhaki> | |||
If multiple Ingresses define different paths for the same host, the behavior depends on the ingress controller. NGINX merges the definitions. | |||
</font> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:18, 22 March 2024
External
Internal
Overview
An Ingress is a mechanism that operates at the application layer of the network stack (HTTP) and brings layer 7 features such as host and path-based routing and cookie-based session affinity to services. Ingress cooperates with services to distribute load to pods. It exposes multiple services through a single IP address, and its implementation differs fundamentally from the implementation of ClusterIP, NodePort and LoadBalancer services. The reasons to use an Ingress include:
- One Ingress can serve multiple services, behind a single public IP address, while each LoadBalancer requires its own native load balancer, each of them requiring their own public IP address.
- Host, paths and cookies can be used to route the request.
The Ingress mechanism consists of an Ingress controller and an Ingress resource.
Playground
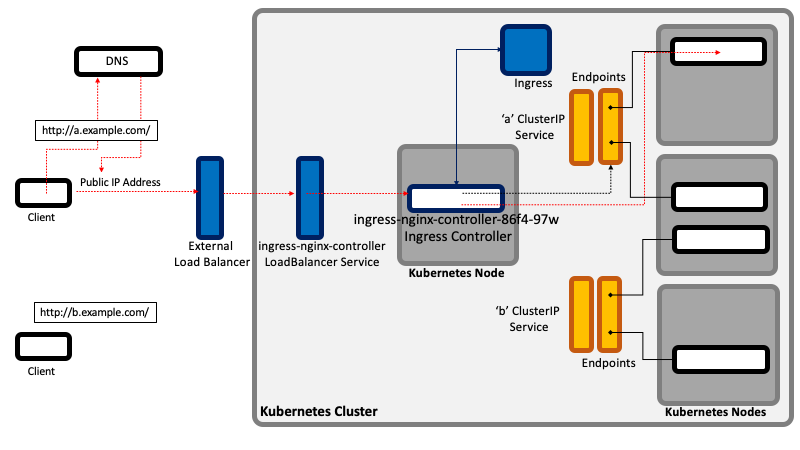
How Ingress Works
A client attempting to access http://a.example.com performs a DNS query and resolves the name to the public IP address of the ingress controller external load balancer. The client then establishes a connection to the ingress external load balancer, specifying "http://a.example.com" in the "Host" header. The ingress controller load balancer forwards the request, via the ingress controller LoadBalancer/NodePort/ClientIP service, to the ingress controller pod. The ingress controller's state was updated when an ingress resource that defines the host "a.example.com" was deployed, and it knows that all requests for "a.example.com" must be forwarded to the "a" ClusterIP service.
When a request with an "a.example.com" Host header arrives, the ingress controller locates the corresponding service, gets the associated Endpoints, picks up a pod and forwards the request to the pod. This is how virtual hosts are handled in web servers.
Note that the ingress controller does not forward the request to the service, but it only uses it to get the associated Endpoints and select a pod.
Ingress Controller
The ingress controller is the process - most likely running as a pod or pods inside the Kubernetes cluster itself - that accepts the HTTP connections, distributes traffic, terminates SSL connections, etc. Some Kubernetes distributions provide an ingress controller as an "add-on". For example, minikube has a minikube addons enable ingress command. If the ingress controller is not provided as add-on, it can be installed. There is a default "ingress-nginx" ingress controller that can be installed in any Kubernetes instance. More details:
The ingress controller deploys as part of its installation a layer 4 service of its own, most likely a LoadBalancer. As such, the ingress controller pod(s) is exposed to external requests via its own LoadBalancer/NodePort/ClusterIP service.
To access a service through an its external name, the external service DNS name must resolve to the public IP address of the load balancer deployed by the ingress controller's LoadBalancer service.
Ingress API Resource
An Ingress is the Kubernetes API resource that declares access to level 4 services and allows configuring this access based on host and path. The ingress controller is notified when new ingress objects are created or when the existing ingress objects are modified and updates its internal state accordingly.
Both "rules" and "paths" elements of an ingress manifest are arrays, so they can contain multiple items. An ingress can map multiple hosts and paths to multiple services. Multiple paths on the same host can be mapped to multiple services.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: example
spec:
rules:
- host: a.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: a
servicePort: 80
- host: b.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: b
servicePort: 80
defaultBackend:
service:
name: c
port:
number: 81
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- a.local
secretName: example-tls-a
Some cloud providers require that the ingress points to a NodePort service, but this is not a Kubernetes requirement.
The ingress must be deployed in the same namespace as the services it serves.
Upon deployment, the hosts served by an ingress, as well as its public address and port can be displayed with the kubectl get ingress command. In the example below, the ingress and the ingress controller have been deployed locally on Docker Desktop Kubernetes, hence the "localhost":
kubectl -n <namespace> get ingress <ingress-name>
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
example a.example.com,b.example.com localhost 80 83s
TLS Support
TODO Kubernetes in Action Section 5.4.4.
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: kubernetes.io/tls
metadata:
name: example-tls
namespace: test-namespace
data:
tls.crt: <base64 encoded cert>
tls.key: <base64 encoded key>
Rewriting Paths
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
spec:
rules:
- host: somehost.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /prod(/|$)(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: service-prod
port:
number: 8080
- path: /stage(/|$)(.*)
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: service-stage
port:
number: 8080
Different Ingresses with Different Path for the Same Host
If multiple Ingresses define different paths for the same host, the behavior depends on the ingress controller. NGINX merges the definitions.