Git Forked Repository Operations: Difference between revisions
(→CLI) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=External= | =External= | ||
* https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/syncing-a-fork | * https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/syncing-a-fork | ||
* https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request-from-a-fork | |||
* https://jarv.is/notes/how-to-pull-request-fork-github | |||
=Internal= | =Internal= | ||
* [[Git_Operations#Procedures|Git Operations]] | * [[Git_Operations#Procedures|Git Operations]] | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
For terminology, see [[Git_Concepts#Upstream_Repository|upstream]]/[[Git_Concepts#Base_Repository|base]] and [[Git_Concepts#Head_Repository|head]] repositories. | For terminology, see [[Git_Concepts#Upstream_Repository|upstream]]/[[Git_Concepts#Base_Repository|base]] and [[Git_Concepts#Head_Repository|head]] repositories. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
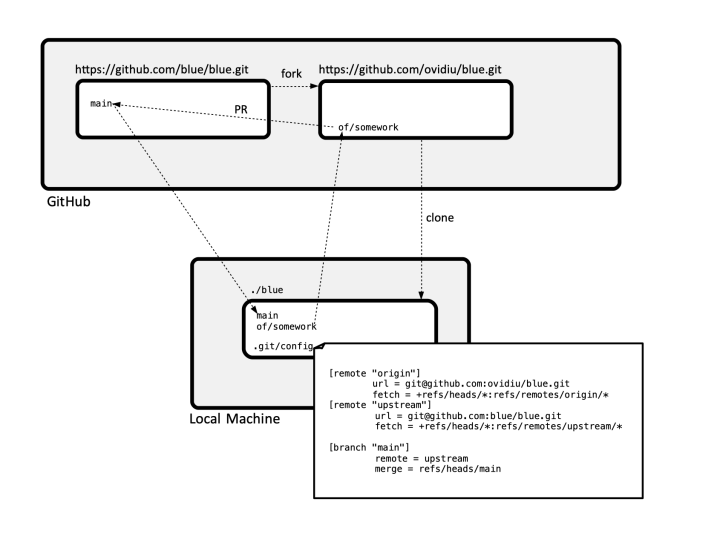
:[[File:A_Typical_GitHub_Fork_Situation.png|720px]] | :[[File:A_Typical_GitHub_Fork_Situation.png|720px]] | ||
=Initial Setup= | |||
=Fork= | ==Fork== | ||
Go to GitHub UI and click on the "Fork" button at the top of the page. Use your own "personal" organization ("ovidiu") to fork into. | Go to GitHub UI and click on the "Fork" button at the top of the page. Use your own "personal" organization ("ovidiu") to fork into. | ||
==Clone== | |||
=Clone= | |||
Clone as usual: | Clone as usual: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
git clone git@github.com:ovidiu/blue.git | git clone git@github.com:ovidiu/blue.git | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Establish Relationships== | |||
= | ===Setup the "upstream" Repository=== | ||
==Setup the "upstream" Repository== | |||
Establish a direct relationship between the local clone and the "upstream" repository. This will allow to pull the latest version of branches directly from the upstream repository. | Establish a direct relationship between the local clone and the "upstream" repository. This will allow to pull the latest version of branches directly from the upstream repository. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 37: | ||
</font> | </font> | ||
This will allow us to fetch directly from "upstream" | To list currently configured remotes, use: | ||
<font size=-2> | |||
[[Git_remote#List_the_Remotes_of_the_Current_Repository|git remote -v]] | |||
</font> | |||
This configuration will allow us to fetch directly from "upstream" | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Configure the "main" Branch to Update From Upstream== | ===Configure the "main" Branch to Update From Upstream=== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 63: | ||
<code>git pull</code> will automatically apply upstream's "main" branch changes to the local main. | <code>git pull</code> will automatically apply upstream's "main" branch changes to the local main. | ||
To fetch PRs, you can optionally add: | |||
<font size=-2> | |||
fetch = +refs/pull/*/head:refs/remotes/upstream/pr/* | |||
</font> | |||
=PR Cycle= | =PR Cycle= | ||
==Send a PR== | ==Send a PR== | ||
Push the commit in the head repository. | |||
PR will show up both in the origin and upstream repository UI. | |||
===From the Origin Repository UI=== | |||
Click "Compare & pull request" | Click "Compare & pull request" | ||
The UI will give you the default choice to send the PR against the base repository while "Create pull request". Use it. | The UI will give you the default choice to send the PR against the base repository while "Create pull request". Use it. | ||
===From the Upstream Repository UI=== | |||
<font color=darkkhaki>TODO</font> | |||
==Merge the PR== | ==Merge the PR== | ||
Upon approval, merge the PR in upstream. | Upon approval, merge the PR in upstream. The branch in the [[Git_Concepts#Fork_.28Head.29_Repository|head repository]] will remain, and it has to be deleted explicitly as described in [[Git_Forked_Repository_Operations#Clean_Up_the_Branch|Clean Up the Branch]] section below. | ||
==Sync the | ==Sync the Repositories after the PR Merge== | ||
There are two repositories to be synced: the origin repository and its local clone. | |||
The local clone can be just simply <code>git pull</code> because its <code>main</code> branch is tracking the upstream repository. | |||
< | The origin repository's <code>main</code> branch can be synced from the GitHub UI: In the origin repository's UI, use "Fetch upstream" button, then "Fetch and Merge". | ||
==Clean Up the Branch== | |||
From the local clone: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
git branch -D of/branch-that-has-just-been-merged | |||
git push origin :of/branch-that-has-just-been-merged | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Additional tidying up: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | ||
git remote prune origin | |||
git remote prune upstream | git remote prune upstream | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 15 April 2024
External
- https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/syncing-a-fork
- https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request-from-a-fork
- https://jarv.is/notes/how-to-pull-request-fork-github
Internal
Overview
For terminology, see upstream/base and head repositories.
The typical GitHub forked repository topology is similar to:
Initial Setup
Fork
Go to GitHub UI and click on the "Fork" button at the top of the page. Use your own "personal" organization ("ovidiu") to fork into.
Clone
Clone as usual:
git clone git@github.com:ovidiu/blue.git
Establish Relationships
Setup the "upstream" Repository
Establish a direct relationship between the local clone and the "upstream" repository. This will allow to pull the latest version of branches directly from the upstream repository.
git remote add upstream git@github.com:blue/blue.git
.git/config will contain:
[remote "upstream"]
url = git@github.com:blue/blue.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/upstream/*
To list currently configured remotes, use:
git remote -v
This configuration will allow us to fetch directly from "upstream"
git fetch upstream
Configure the "main" Branch to Update From Upstream
git fetch upstream
git branch --set-upstream-to=upstream/main main
This will configure the local "main" branch to track upstream's "main" branch. The .git/config will look like:
[branch "main"]
remote = upstream
merge = refs/heads/main
git pull will automatically apply upstream's "main" branch changes to the local main.
To fetch PRs, you can optionally add:
fetch = +refs/pull/*/head:refs/remotes/upstream/pr/*
PR Cycle
Send a PR
Push the commit in the head repository.
PR will show up both in the origin and upstream repository UI.
From the Origin Repository UI
Click "Compare & pull request"
The UI will give you the default choice to send the PR against the base repository while "Create pull request". Use it.
From the Upstream Repository UI
TODO
Merge the PR
Upon approval, merge the PR in upstream. The branch in the head repository will remain, and it has to be deleted explicitly as described in Clean Up the Branch section below.
Sync the Repositories after the PR Merge
There are two repositories to be synced: the origin repository and its local clone.
The local clone can be just simply git pull because its main branch is tracking the upstream repository.
The origin repository's main branch can be synced from the GitHub UI: In the origin repository's UI, use "Fetch upstream" button, then "Fetch and Merge".
Clean Up the Branch
From the local clone:
git branch -D of/branch-that-has-just-been-merged
git push origin :of/branch-that-has-just-been-merged
Additional tidying up:
git remote prune origin
git remote prune upstream