RHEL 7 Virtualization Host Installation: Difference between revisions
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
==Enable libvirt-guests== | ==Enable libvirt-guests== | ||
Enable [[Linux_Virtualization_Concepts#libvirt-guests|libvirt-guests]] and configure guest startup/shutdown behavior: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
systemctl enable libvirt-guests | systemctl enable libvirt-guests | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{Internal|Linux_Virtualization_Configuration#Configure_Guests_to_Gracefully_Shut_Down|Configure Guests to Gracefully Shut Down]] | |||
{{Internal|Linux_Virtualization_Configuration#Configure_Guests_to_Start_at_Boot|Configure Guests to Start at Boot]] | |||
=Guest Creation= | =Guest Creation= | ||
Create guest as needed, on command-line with [[virt-install]] or from previously generated XML definitions with [[virsh define]]. | Create guest as needed, on command-line with [[virt-install]] or from previously generated XML definitions with [[virsh define]]. | ||
Revision as of 20:45, 27 June 2017
Internal
Relevance
- RHEL 7.3
Virtualization Host Prerequisites
The host requires minimum 6 GB of free disk space and minimum 2 GB or RAM.
Installed with 50 GB root partition, 4 GB RAM and 4 GB swap.
Virtualization Host Installation
if the virtualization host runs on a Dell server, install the host operating system following the procedure described here:
The procedure will update the Dell firmware and drivers and then will pass control to the native O/S installer, that should be driven as described below. Note that the only areas in which the virtualization host installation procedure differs from a regular server installation procedure is Storage Provisioning and Virtualization Host-Specific Configuration. In consequence:
- first configure storage, follow the Storage Provisioning instructions, below.
- then execute the normal server installation procedure RHEL 7 Installation.
- then return to Virtualization Host-Specific Configuration.
Storage Provisioning
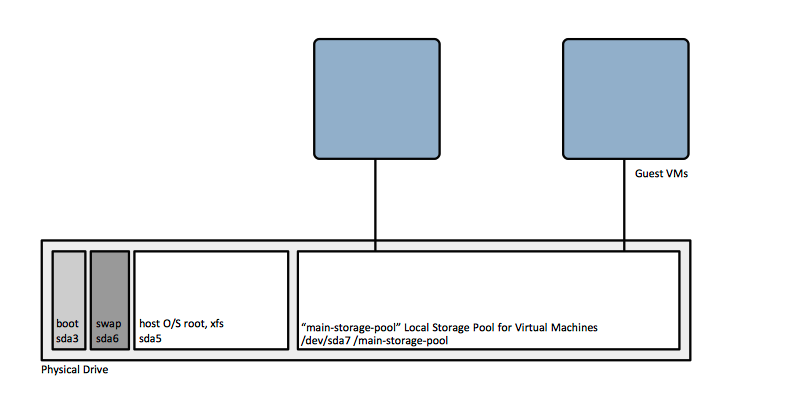
Mount Point: /boot capacity 1024 MiB, standard partition xfs file system (/dev/sda3)
Mount Point: / capacity 50 GiB, standard partition xfs file system (/dev/sda5)
Mount Point: /swap capacity 4 GiB (/dev/sda6)
Leave the rest of the space unallocated, will create later the local storage pool for virtual machines using one of the procedures described here: KVM Storage Pool Configuration.
Virtualization Host-Specific Configuration
Virtualization Packages
yum install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt virt-manager libguestfs-tools libvirt-client virt-install libguestfs-tools-c virt-top virt-what
Among other things, installing these packages enables libvirtd to start at boot, automatically.
Virtualization Host Storage Provisioning
Create a host storage pool and storage volumes, as described here:
Virtualization Host Network Configuration
Configure virtualization host networking as described here:
Enable libvirt-guests
Enable libvirt-guests and configure guest startup/shutdown behavior:
systemctl enable libvirt-guests
{{Internal|Linux_Virtualization_Configuration#Configure_Guests_to_Gracefully_Shut_Down|Configure Guests to Gracefully Shut Down]] {{Internal|Linux_Virtualization_Configuration#Configure_Guests_to_Start_at_Boot|Configure Guests to Start at Boot]]
Guest Creation
Create guest as needed, on command-line with virt-install or from previously generated XML definitions with virsh define.