Deque: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
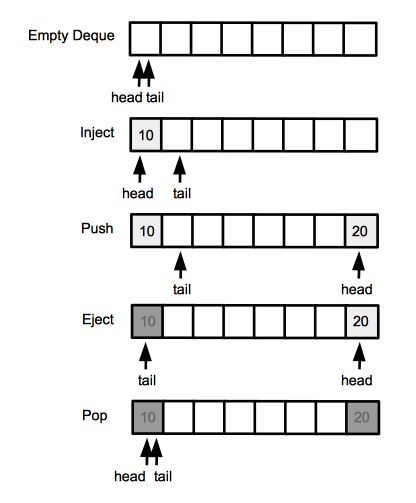
The following implementation uses an array of length n for storage. Because we want to use all n elements of the array for storage of the deque elements, we need an extra boolean member variable "full" to tell whether the structure is empty or full - in both cases the head pointer overlaps the tail pointer. | The following implementation uses an array of length n for storage. Because we want to use all n elements of the array for storage of the deque elements, we need an extra boolean member variable "full" to tell whether the structure is empty or full - in both cases the head pointer overlaps the tail pointer. | ||
[[File:Deque.png]] | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='java'> | <syntaxhighlight lang='java'> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 21:02, 11 August 2018
External
Internal
Overview
A deque is a dynamic set that generalizes the concept of queue. The elements can be enqueued and dequeued both from the head and the tail of the deque. The INSERT and DELETE operations have each two versions:
- insert to head or push.
- delete from head or pop.
- insert to tail or inject.
- delete from tail or eject.
Implementation
The following implementation uses an array of length n for storage. Because we want to use all n elements of the array for storage of the deque elements, we need an extra boolean member variable "full" to tell whether the structure is empty or full - in both cases the head pointer overlaps the tail pointer.