Tree Representation in Memory: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
[[Tree_Concepts#Rooted_Tree|Rooted trees]] can be implemented in several ways: | [[Tree_Concepts#Rooted_Tree|Rooted trees]] can be implemented in several ways: | ||
* Use [[#Representing_Rooted_Trees_as_Linked_Data_Structures|linked data structures]] | * Use [[#Representing_Rooted_Trees_as_Linked_Data_Structures|linked data structures]] | ||
* Use a [[Heap#Overview|heap]] structure in an array. | * Use a [[Heap#Overview|heap]] structure in an array. | ||
Revision as of 21:27, 9 October 2021
Internal
Overview
Rooted trees can be implemented in several ways:
- Use linked data structures
- Use a heap structure in an array.
Representing Rooted Trees as Linked Data Structures
Each tree node is represented by an object that has a key attributed, and pointers to other nodes, which vary depending on the tree type.
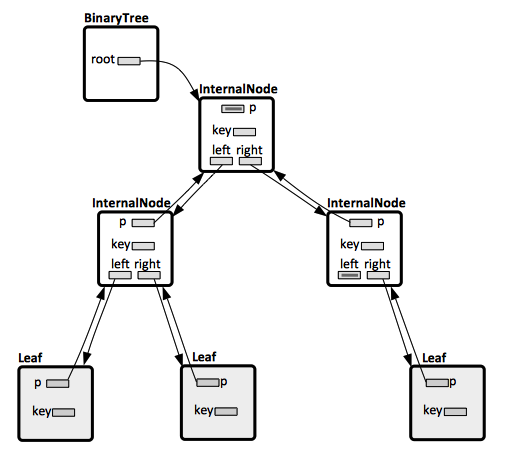
Representing Binary Trees
There are three pointers:
- p, which points to the parent node. Only the tree's root has a null parent.
- left and right, which point to the left and the right child. If the node has no left child, left is NULL. If the node has no right child, right is NULL.
Representing Trees whose Nodes have an Arbitrary Number of Children
One option to represent trees whose nodes have an arbitrary number of children is to extend the scheme used for representing binary tree to any class of trees in which the number of children in each node is at most some constant k: we replace the left and right attributes by child0, child1, ... childk-1. However, this is not ideal: we cannot represent an unbounded number of children, and also when the number of children k is bounded by some large constant, but most nodes have a small number of children, we waste a lot of memory.
Another scheme to represent an arbitrary number of children is left-child, right-sibling representation. Instead of having a pointer to each of its children, each node has only three pointers:
- parent
- left-child points to the leftmost child
- right-sibling points to the node's sibling immediately to the right.
