Binary Search Trees: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
A binary search tree is a [[Tree_Concepts#Binary_Tree|binary tree]] that has the Binary Search Tree Property. A binary search tree is represented in memory using three pointers: left child, right child and the parent. More details on binary tree representation in memory are available here: {{Internal|Tree_Representation_in_Memory#Binary_Trees|Binary Tree Representation in Memory}} | A binary search tree is a [[Tree_Concepts#Binary_Tree|binary tree]] that has the Binary Search Tree Property. A binary search tree is represented in memory using three pointers: left child, right child and the parent. More details on binary tree representation in memory are available here: {{Internal|Tree_Representation_in_Memory#Binary_Trees|Binary Tree Representation in Memory}} | ||
=Binary Search Tree Property= | |||
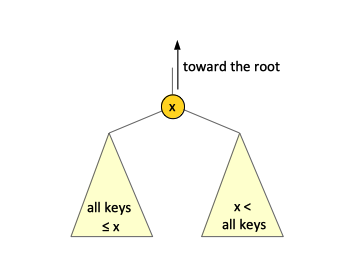
The fundamental property of the binary search tree, called the '''Binary Search Tree Property''': | |||
{{Note|For every single node of a binary search tree, if the node has a key value, then all of the keys stored in the '''left subtree''' should be less than the node's key value and all of the keys stored in the '''right subtree''' should be bigger than the node's key value. This property holds not only at the root, but in every single node of the three.}} | |||
::[[File:Binary_Search_Tree_Property.png|355px]] | |||
Note that the Binary Search Tree Property is different from the [[Heap#The_Heap_Property|Heap Property]]. Search tree are designed so we can search easily through them, unlike heaps that are designed to find the minimum (or maximum) easily. | |||
<font color=darkkhaki>TODO [[CLRS]] Page 286.</font> | |||
Revision as of 03:53, 13 October 2021
Internal
Overview
A binary search tree is a binary tree that has the Binary Search Tree Property. A binary search tree is represented in memory using three pointers: left child, right child and the parent. More details on binary tree representation in memory are available here:
Binary Search Tree Property
The fundamental property of the binary search tree, called the Binary Search Tree Property:
For every single node of a binary search tree, if the node has a key value, then all of the keys stored in the left subtree should be less than the node's key value and all of the keys stored in the right subtree should be bigger than the node's key value. This property holds not only at the root, but in every single node of the three.
Note that the Binary Search Tree Property is different from the Heap Property. Search tree are designed so we can search easily through them, unlike heaps that are designed to find the minimum (or maximum) easily.
TODO CLRS Page 286.