System Design: Difference between revisions
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
::::[[File:ATypicalSystem.png|397px]] | ::::[[File:ATypicalSystem.png|397px]] | ||
The clients can be web applications or mobile applications. A web application uses a combination of server-side logic written in a language as Java or Python and packaged and deployed as containerized services to handle business logic and storage, and a client-side language as HTML or [[JavaScript]] for presentation. A mobile application uses the same type of backend infrastructure, but a device-specific language to implement the client. In both cases, the clients send requests over HTTP. The server returns the response as part of the same HTTP request/response pair, either a HTML page to be rendered or | The clients can be web applications or mobile applications. A web application uses a combination of server-side logic written in a language as Java or Python and packaged and deployed as containerized services to handle business logic and storage, and a client-side language as HTML or [[JavaScript]] for presentation. A mobile application uses the same type of backend infrastructure, but a device-specific language to implement the client. In both cases, the clients send requests over HTTP. The server returns the response as part of the same HTTP request/response pair, either a HTML page to be rendered or [[JSON]]-serialized data. | ||
<font color=darkkhaki> | <font color=darkkhaki> | ||
Revision as of 01:58, 7 November 2021
External
- Episode 06 Unqualified Engineer - Jackson Gabbard: Intro to Architecture and Systems Design Interviews https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZgdS0EUmn70
Internal
Overview
The goals of system design is to build software systems that first and foremost are correct, in that the system correctly implements the functions it was built to implement. Additionally, they should aim to maximize reliability, scalability and maintainability.
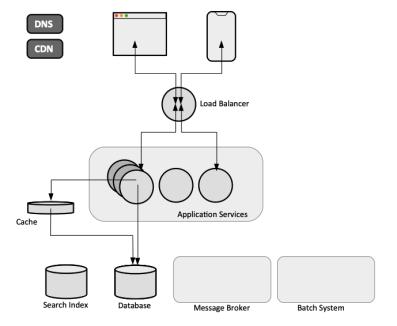
A Typical System
Many web and mobile applications in use today are conceptually similar to the generic system described below. The functionality differs, as well as reliability, scalability and maintainability requirements, but most systems share at least several of the elements described here. They have mobile and browser clients, communicate with the backend via HTTP or WebSocket protocols, include a business logic layer deployed as monoliths or microservices, in most cases in containers managed by a container orchestration system like Kubernetes, persist their data in databases, either relational or NoSQL, use caches to speed up reads, and rely on message brokers or streaming systems for asynchronous processing and better decoupling. Depending on the actual functionality of the system, these bits and pieces can be implemented as different products and connected in all kind of ways.
The clients can be web applications or mobile applications. A web application uses a combination of server-side logic written in a language as Java or Python and packaged and deployed as containerized services to handle business logic and storage, and a client-side language as HTML or JavaScript for presentation. A mobile application uses the same type of backend infrastructure, but a device-specific language to implement the client. In both cases, the clients send requests over HTTP. The server returns the response as part of the same HTTP request/response pair, either a HTML page to be rendered or JSON-serialized data.
Request flow. Write path. Read path.
Aims
Correctness. Ensured via testing.
Reliability. Discuss difference between reliability and high availability.
Scalability
Maintainability
Operations
Logs
Monitoring
Deployment
TODO
- Process and redistribute: Distributed Systems
- Clean Architecture https://www.amazon.com/Clean-Architecture-Craftsmans-Software-Structure/dp/0134494164/
- https://medium.com/@i.gorton/six-rules-of-thumb-for-scaling-software-architectures-a831960414f9
- http://highscalability.com
- Harvard Scalability Class David Malan https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-W9F__D3oY4
- https://www.lecloud.net/post/7295452622/scalability-for-dummies-part-1-clones
- https://www.lecloud.net/post/7994751381/scalability-for-dummies-part-2-database
- https://www.lecloud.net/post/9246290032/scalability-for-dummies-part-3-cache
- https://www.lecloud.net/post/9699762917/scalability-for-dummies-part-4-asynchronism
- https://www.hiredintech.com/classrooms/system-design/lesson/61
- Learning/System Design/*.pdf
- https://github.com/checkcheckzz/system-design-interview
- https://github.com/donnemartin/system-design-primer
- https://github.com/mmcgrana/services-engineering
- https://github.com/orrsella/soft-eng-interview-prep/blob/master/topics/system-architecture.md
- https://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=3480470
- https://blog.pramp.com/how-to-succeed-in-a-system-design-interview-27b35de0df26
- https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2021/09/21/distributed-transaction-patterns-microservices-compared
Subjects
- State Transition Diagram
- Distributed Systems
- Schemaless: Fowler https://martinfowler.com/articles/schemaless/
Organizatorium
- Capacity estimation