Infrastructure Code Continuous Delivery Concepts: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
=<span id='Pipeline'></span><span id='Infrastructure_Delivery_Pipelines'></span>Infrastructure Delivery Pipeline= | =<span id='Pipeline'></span><span id='Infrastructure_Delivery_Pipelines'></span>Infrastructure Delivery Pipeline= | ||
== | :[[File:Infrastructure_Delivery_Pipeline.png]] | ||
==Activities== | |||
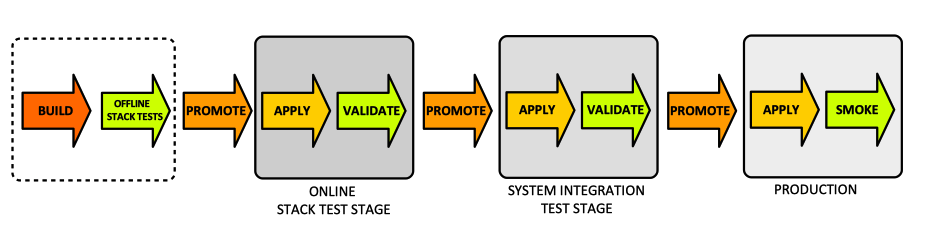
A infrastructure delivery pipeline implies multiple types of activities, grouped in stages: | A infrastructure delivery pipeline implies multiple types of activities, grouped in stages: | ||
===Build=== | ===Build=== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
===Apply=== | ===Apply=== | ||
===Validate=== | ===Validate=== | ||
==Stages== | |||
Revision as of 00:30, 23 January 2022
External
Internal
Overview
The delivery pipeline metaphor describes how a change in the infrastructure code progresses from the person that makes the change all the way to production.
Reconcile with Continuous Delivery.
Infrastructure Delivery Pipeline
Activities
A infrastructure delivery pipeline implies multiple types of activities, grouped in stages:
Build
The build stage compiles application code, runs unit tests and integration tests, in as offline and online testes, and publishes a deployable artifact in a repository.
Offline Tests
Online Tests
In a dedicated environment.
Promote
Apply
Validate
Stages
TO CONTINUE: IaC Chapter 8 Core Practice: Continuously Test and Deliver → Infrastructure Delivery Pipelines.
TO INTEGRATE:
Organizatorium
- Modeling Deployment Pipelines: Build Propagation using Fan-in/Fan-out https://www.gocd.org/2017/04/17/build-propagation-using-fan-in-fan-out.html