Bash * and @ Relative to Array Elements: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "=Internal= * <tt>$@</tt> * <tt>$*</tt> =Overview=") |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Internal= | =Internal= | ||
* [[Bash_Concepts#$@|<tt>$@</tt>]] | * [[Bash_Concepts#$@|<tt>"$@"</tt>]] | ||
* [[Bash_Concepts#$*|<tt>$*</tt>]] | * [[Bash_Concepts#$*|<tt>$*</tt>]] | ||
* [[Bash_Arrays#Reference_All_Indexed_Array_Elements|Get All Indexed Array Elements]] | |||
* [[Bash_Arrays#Get_All_Associative_Array_Keys|Get All Associative Array Keys]] | |||
* [[Bash_Arrays#Get_All_Associative_Array_Values|Get All Associative Array Values]] | |||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
<code>*</code> and <code>@</code> are bash syntax elements that tokenize arrays. They are used to process command line argument (<code>$*</code> and <code>"$@"</code>), [[Bash_Arrays#Reference_All_Indexed_Array_Elements|values for indexed arrays]], [[Bash_Arrays#Get_All_Associative_Array_Keys|keys]] and [[Bash_Arrays#Get_All_Associative_Array_Values|values]] for associative arrays, etc. | |||
The difference between these two syntax elements becomes apparent when the array elements contain spaces, as explained below. | |||
=<tt>*</tt>= | |||
Each element in the array is represented as an individual string. The arguments that contain spaces are tokenized, and the spaces are discarded. In other words, the arguments that contain spaces are not joined together, but handled as different tokens. | |||
In case of command line arguments handled as such: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
for i in $*; do | |||
echo ${i} | |||
done | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
calling the program with: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
./test.sh "A B" "C D" | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
outputs: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
A | |||
B | |||
C | |||
D | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The behavior is similar in case of getting indexed array values or associative array keys or values: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
declare -a some_array | |||
some_array[0]="A B" | |||
some_array[1]="C D" | |||
for i in ${some_array[*]}; do | |||
echo ${i} | |||
done | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
outputs: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
A | |||
B | |||
C | |||
D | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=<tt>"@"</tt>= | |||
The <code>"@"</code> syntax preserves array elements that contain spaces as individual tokens. | |||
In case of command line arguments handled as such: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
for i in "$@"; do | |||
echo ${i} | |||
done | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
calling the program with: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
./test.sh "A B" "C D" | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
outputs: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
A B | |||
C D | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The behavior is similar in case of getting indexed array values or associative array keys or values: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
declare -a some_array | |||
some_array[0]="A B" | |||
some_array[1]="C D" | |||
for i in "${some_array[@]}"; do | |||
echo ${i} | |||
done | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
outputs: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
A B | |||
C D | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=<tt>@</tt>= | |||
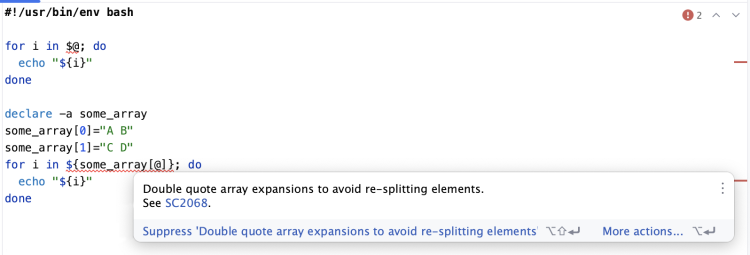
Using <code>@</code> without double-quote enclosure to iterate over array elements is signaled as an error by bash static syntax checkers: | |||
<br> | |||
::[[File:Bash_@.png|750px]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 1 April 2024
Internal
- "$@"
- $*
- Get All Indexed Array Elements
- Get All Associative Array Keys
- Get All Associative Array Values
Overview
* and @ are bash syntax elements that tokenize arrays. They are used to process command line argument ($* and "$@"), values for indexed arrays, keys and values for associative arrays, etc.
The difference between these two syntax elements becomes apparent when the array elements contain spaces, as explained below.
*
Each element in the array is represented as an individual string. The arguments that contain spaces are tokenized, and the spaces are discarded. In other words, the arguments that contain spaces are not joined together, but handled as different tokens.
In case of command line arguments handled as such:
for i in $*; do
echo ${i}
done
calling the program with:
./test.sh "A B" "C D"
outputs:
A
B
C
D
The behavior is similar in case of getting indexed array values or associative array keys or values:
declare -a some_array
some_array[0]="A B"
some_array[1]="C D"
for i in ${some_array[*]}; do
echo ${i}
done
outputs:
A
B
C
D
"@"
The "@" syntax preserves array elements that contain spaces as individual tokens.
In case of command line arguments handled as such:
for i in "$@"; do
echo ${i}
done
calling the program with:
./test.sh "A B" "C D"
outputs:
A B
C D
The behavior is similar in case of getting indexed array values or associative array keys or values:
declare -a some_array
some_array[0]="A B"
some_array[1]="C D"
for i in "${some_array[@]}"; do
echo ${i}
done
outputs:
A B
C D
@
Using @ without double-quote enclosure to iterate over array elements is signaled as an error by bash static syntax checkers: