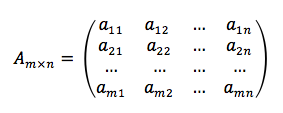Matrix: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
A matrix is a two-dimensional array. Its content is organized in rows and columns. | |||
[[Image:Matrix.png]] | |||
n | where ''m'' represents the number of rows and ''n'' represents the number of columns. | ||
=Matrix Multiplication= | =Matrix Multiplication= | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
Two matrices can be multiplied if the number of columns of the first operand is equal with the number of rows of the second operand: | Two matrices can be multiplied if the number of columns of the first operand is equal with the number of rows of the second operand: | ||
[[Image:MatrixMultiplication.png]] | :[[Image:MatrixMultiplication.png]] | ||
Matrix multiplication is general not commutative. | Matrix multiplication is in general not commutative. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:53, 28 December 2017
Internal
Overview
A matrix is a two-dimensional array. Its content is organized in rows and columns.
where m represents the number of rows and n represents the number of columns.
Matrix Multiplication
Two matrices can be multiplied if the number of columns of the first operand is equal with the number of rows of the second operand:
Matrix multiplication is in general not commutative.