Search Tree Rotation: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "=External= =Internal= * Binary Search Trees") |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=External= | =External= | ||
* https://www.coursera.org/learn/algorithms-graphs-data-structures/lecture/JV7KI/rotations-advanced-optional | |||
=Internal= | =Internal= | ||
* [[Binary_Search_Trees#Rotation|Binary Search Trees]] | * [[Binary_Search_Trees#Rotation|Binary Search Trees]] | ||
=Overview= | |||
Rotations are a set of primitives common to all binary search tree implementations, which preserve the [[Binary_Search_Trees#Binary_Search_Tree_Property|Binary Search Tree Property]] while locally rebalancing subtrees at a node in O(1) time. There are left rotations and right rotations. When invoking a rotation, is on a parent-child pair of a search tree. If it is the right child of the parent, use a left rotation. If it is the left child, use a right rotation. | |||
{{Note|Rotations preserve the [[Binary_Search_Trees#Binary_Search_Tree_Property|Binary Search Tree Property]].}} | |||
=Left Rotation= | |||
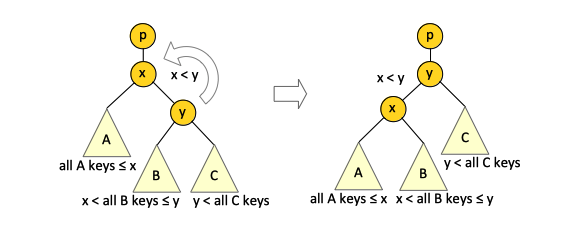
The goal of the left rotation is to invert the relationship between the nodes x and y: y becomes the parent and x the child, while preserving the binary search tree property. | |||
:[[File:Left_Rotation.png|581px]] | |||
=Right Rotation= | |||
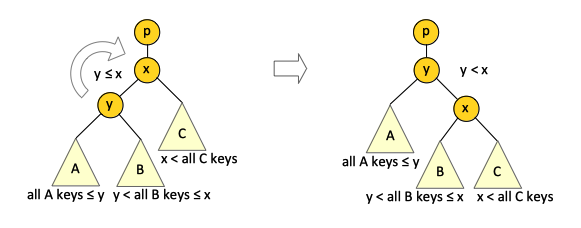
The goal of the right rotation is to invert the relationship between the nodes x and y: y becomes the parent and x the child, while preserving the binary search tree property. | |||
:[[File:Right_Rotation.png|581px]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:18, 13 October 2021
External
Internal
Overview
Rotations are a set of primitives common to all binary search tree implementations, which preserve the Binary Search Tree Property while locally rebalancing subtrees at a node in O(1) time. There are left rotations and right rotations. When invoking a rotation, is on a parent-child pair of a search tree. If it is the right child of the parent, use a left rotation. If it is the left child, use a right rotation.
Rotations preserve the Binary Search Tree Property.
Left Rotation
The goal of the left rotation is to invert the relationship between the nodes x and y: y becomes the parent and x the child, while preserving the binary search tree property.
Right Rotation
The goal of the right rotation is to invert the relationship between the nodes x and y: y becomes the parent and x the child, while preserving the binary search tree property.