Events: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
* [[projects#Projects|projects]] | * [[projects#Projects|projects]] | ||
* [[Business Scenario-Based Performance Monitoring and Diagnosis]] | * [[Business Scenario-Based Performance Monitoring and Diagnosis]] | ||
* [[clad]] | |||
* [[pt]] | * [[pt]] | ||
* [[DataBot]] | |||
=Deprecation Notice= | |||
Events Core (events-core-deprecated) is deprecated and it is being replaced by [[Events-api|Events API]]. | |||
At the time of the writing, Events Core still contains useful functionality (multi-component event processing system, HTTPD log parsing, etc.). These will be migrated to their own projects as needed. | |||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
| Line 9: | Line 17: | ||
"events" is Java library and a command line tool that parses various event stream sources (logs, Java runtimes), turns them into events streams and assists with analysis or makes it easy to feed into R. | "events" is Java library and a command line tool that parses various event stream sources (logs, Java runtimes), turns them into events streams and assists with analysis or makes it easy to feed into R. | ||
The project's artifact is an installable command line utility. | The project's artifact is an installable command line utility. Details on how to install it are available in the [[events User Manual#Installation|User Manual's Installation section]]. | ||
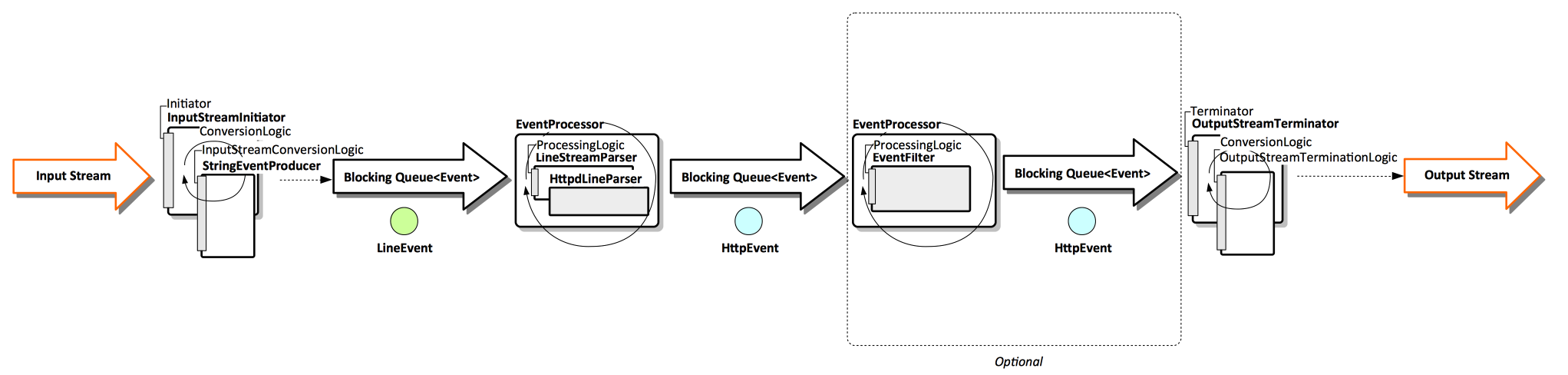
Conceptually, an <tt>events</tt> runtime can be seen as a pipeline that processes the input steam and produces an output stream. The input stream is handled by the ''initiator'' component, whose conversion logic is pluggable. The events thus generated are asynchronously sent into an ''event processor'', whose processing logic is pluggable as well. After processing, the resulted events - which can be of a different type than the events produced by the initiator - are asynchronously sent to the ''terminator'' component, which has a chance to convert the events for output or termination of the stream. | Conceptually, an <tt>events</tt> runtime can be seen as a pipeline that processes the input steam and produces an output stream. The input stream is handled by the ''initiator'' component, whose conversion logic is pluggable. The events thus generated are asynchronously sent into an ''event processor'', whose processing logic is pluggable as well. After processing, the resulted events - which can be of a different type than the events produced by the initiator - are asynchronously sent to the ''terminator'' component, which has a chance to convert the events for output or termination of the stream. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 23: | ||
[[Image:eventsConcepts.png]] | [[Image:eventsConcepts.png]] | ||
O/S level performance events can be collected and channeled by [[DataBot]]. | |||
= | =Subjects= | ||
< | * <span id='GitHub'></span>GitHub https://github.com/NovaOrdis/events | ||
* <span id='User_Manual'></span>[[events User Manual]] | |||
</ | * <span id='Development'></span>[[events Development]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:26, 29 July 2017
Internal
Deprecation Notice
Events Core (events-core-deprecated) is deprecated and it is being replaced by Events API.
At the time of the writing, Events Core still contains useful functionality (multi-component event processing system, HTTPD log parsing, etc.). These will be migrated to their own projects as needed.
Overview
"events" is Java library and a command line tool that parses various event stream sources (logs, Java runtimes), turns them into events streams and assists with analysis or makes it easy to feed into R.
The project's artifact is an installable command line utility. Details on how to install it are available in the User Manual's Installation section.
Conceptually, an events runtime can be seen as a pipeline that processes the input steam and produces an output stream. The input stream is handled by the initiator component, whose conversion logic is pluggable. The events thus generated are asynchronously sent into an event processor, whose processing logic is pluggable as well. After processing, the resulted events - which can be of a different type than the events produced by the initiator - are asynchronously sent to the terminator component, which has a chance to convert the events for output or termination of the stream.
O/S level performance events can be collected and channeled by DataBot.