DataBot User Manual: Difference between revisions
| Line 239: | Line 239: | ||
'''output.append''' - true/false. Indicates whether to append to an already existing output file or to overwrite the existing file. The default value is "true" (append); this configuration will allow accumulation of historical data. Every time DataBot is restarted in "append" mode, a new header line will be inserted in the file. | '''output.append''' - true/false. Indicates whether to append to an already existing output file or to overwrite the existing file. The default value is "true" (append); this configuration will allow accumulation of historical data. Every time DataBot is restarted in "append" mode, a new header line will be inserted in the file. | ||
===Generic Consumers==== | |||
... | |||
consumers: | |||
- io.novaordis.SomeConsumer | |||
... | |||
==Metrics== | ==Metrics== | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 9 January 2018
Internal
Overview
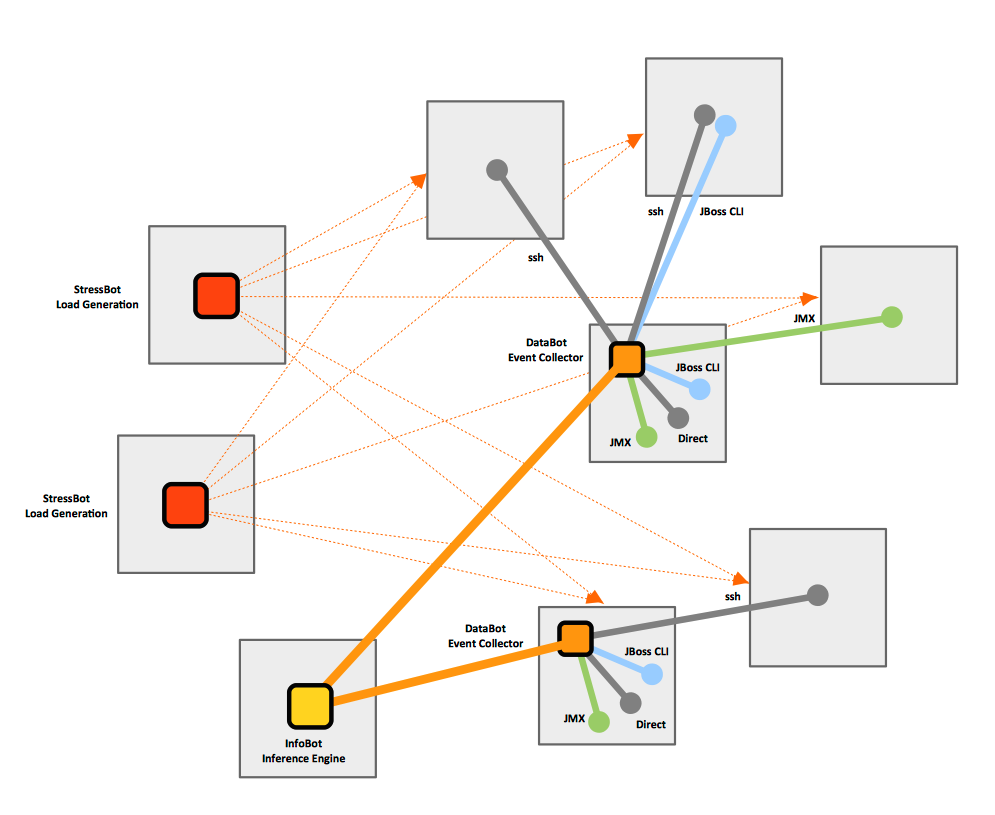
DataBot is a low-overhead O/S level event collector that generates events-compatible events. DataBot is designed to run as a system daemon, indefinitely. Only one DataBot instance per VM is necessary. DataBot will collect timed events and channel them to various destinations, such as files, network, etc. It is capable of collecting memory, CPU, etc. usage statistics, as well as WildFly management domain model and JMX metrics.
Concepts
Metric Definition
Metric Source
Data Consumer
Installation
Download the stable release from
The release consists in a ZIP file with a name matching "databot-<version>.zip".
Unzip the release file in a conventional binary directory, such as /opt or /usr/local. An "databot-<version>" sub-directory will be created.
Add .../databot-<version>/bin to PATH.
DataBot needs a Java VM to run. It will attempt to use, in this order:
- Value of "DATABOT_JAVA_HOME" environment variable, if set.
- Value of "JAVA_HOME" environment variable, if set.
- The "java" executable found in path.
Upgrade
Unzip the release ZIP in the parent directory of the previous DataBot installation and then redirect the symbolic link from the previous release to the current one.
Assuming that DataBot 1.0 is installed in /opt/databot-1.0, the sequence to upgrade to DataBot 1.1 consists of the following steps:
cd /opt unzip databot-1.1.zip # remove the symbolic link to the previous release: rm databot # re-create the symbolic link to the new release: ln -s ./databot-1.1 databot
Configuration File
Choose a directory to store the configuration file.
If the configuration will be shared by multiple users and there will be used by just one DataBot instance on the system, /etc/databot is a recommended location. Otherwise, each user could maintain an individual configuration file in ~/.databot (recommended) or a directory of their choosing. The location of the configuration file should be exposed as the value of the DATABOT_CONF environment variable in the environment of the user who will execute DataBot. If no DATABOT_CONF environment variable is defined, DataBot will attempt to read ~/.databot/databot.yaml.
The configuration file location can be overridden from command line using -c|--configuration= options. If one of these options is specified, the environment variables and default locations are ignored.
Regardless of how the configuration file is declared, DataBot will fail if the file is not found. For details on the configuration file syntax see Configuration section below.
Complete any of target-specific configuration procedures, if they apply.
Usage
databot [status|stop]
If a DataBot process is already running in the background, an attempt to start another DataBot instance will fail.
To start an instance that runs in foreground, use -f|--foreground command line option. In foreground mode, the output is switched automatically from the configured file destination to /dev/stdout and the output.file configuration, as described below, is ignored.
Commands
help
Display in-line help.
version
Display version information.
status
Display whether a background DataBot process already runs on the system. If a process is found running, the command provides more information about it (such as the PID).
stop
Stop the background DataBot process, if running.
Options
-c|--configuration
-f|--foreground
Run the command in foreground and automatically switch the output from the configured file destination to /dev/stdout.
-v|--verbose
Turns on DEBUG logging at stdout.
-d|--debug
Start the JVM in debug mode, so it can be accessed by a debugger. It also turns on DEBUG logging.
Configuration
#
# DataBot configuration file
#
#
# sampling interval (in seconds)
#
sampling.interval: 20
#
# override embedded logging configuration
#
logging:
file: /var/log/databot/databot.log
loggers:
- io.novaordis: INFO
- io.novaordis.utilities.os: INFO
sources:
local-jboss-instance:
type: jboss-controller
host: localhost
port: 9999
username: admin
password: admin123
classpath:
- /Users/ovidiu/runtime/jboss-eap-6.4.15/bin/client/jboss-cli-client.jar
remote-jboss-instance:
type: jboss-controller
host: other-host
port: 10101
username: admin
password: something
classpath:
- /Users/ovidiu/runtime/jboss-eap-6.4.15/bin/client/jboss-cli-client.jar
local-jboss-over-jmx:
type: jmx
host: localhost
port: 9999
classpath:
- /Users/ovidiu/runtime/jboss-eap-6.4.15/bin/client/jboss-cli-client.jar
remote-jboss-over-jmx:
type: jmx
host: some-jmx-host
port: 4447
username: admin
password: something
classpath:
- /Users/ovidiu/runtime/jboss-eap-6.4.15/bin/client/jboss-cli-client.jar
#
# output configuration
#
output:
file: /var/log/databot/databot.csv
append: true
#
# metrics
#
metrics:
- PhysicalMemoryFree
- PhysicalMemoryTotal
- CpuUserTime
- CpuKernelTime
- CpuIdleTime
- ${local-jboss-instance}/subsystem=messaging/hornetq-server=default/jms-queue=DLQ/message-count
- jmx://admin:admin123@localhost:9999/jboss.as:subsystem=messaging,hornetq-server=default,jms-queue=DLQ/messageCount
Variable Support
The configuration file allows declaration and reference of variables.
Some configuration elements cause implicit variable declaration, and references to those variables can be used in subsequence configuration element. An example is a metric source: declaring a metric source enable metric definitions to refer to that metric source name as a variable. When the metric definition is parsed, the variable is evaluated to the metric source's address.
Example:
sources:
some-jmx-source:
type: jmx
host: ...
...
...
metrics:
${some-jmx-source)/some.domain:....
Environment variables can also be referred to from the configuration file.
Global Options
sampling.interval
Represents the interval, in seconds, between two successive readings. If not specified, the default value is 10 seconds.
If configured with 0, DataBot will read once and exit.
Sources
This section specifies configuration details for metric sources to be queried for metrics, such as the address, etc.
The section is optional, as the metric sources can be specified in-line in the metric definition. However, when a large number of metric definitions are declared, it may become cumbersome to specify the full address of the source within each definition, so declaring it in the "sources" section and then referring to it by name is a better alternative.
Each source declared in the "sources" section must be named, and the names must be unique: if two sources are listed with the same name, only the second value is considered, the first one being overwritten by the second.
Data Consumers
Stdout
The output is sent to /dev/stdout:
... output: stdout ...
Output CSV File
... output: file: /tmp/databot.csv append: true ...
output.file - the name of the output file. If not specified, the default value is /tmp/databot.csv. Note that if --foreground (or -f) option is used, the output will forcibly send to /dev/stdout, regardless of the value of 'output.file' configuration parameter.
output.append - true/false. Indicates whether to append to an already existing output file or to overwrite the existing file. The default value is "true" (append); this configuration will allow accumulation of historical data. Every time DataBot is restarted in "append" mode, a new header line will be inserted in the file.
Generic Consumers=
... consumers: - io.novaordis.SomeConsumer ...
Metrics
This section contains the definitions of the metrics to be collected.
metrics - comma-separated list of the definitions for the metrics to be collected from the system.
Example:
metrics=PhysicalMemoryUsed,CpuUserTime,jboss:/subsystem=web/connector=http/bytesReceived
For a complete list of supported metrics, syntax details and extensive documentation, see https://kb.novaordis.com/index.php/DataBot_Metric_Reference
jboss.home - the path to a locally accessible JBoss instance. If it needs to monitor JBoss CLI metrics, DataBot must be configured to detect and use the libraries from a JBoss instance it has access to (it does not ship with the required JARs, as those may be different depending on the version of the target JBoss instance. In order to enable DataBot to build the classpath fragment, jboss_home must be specified in the configuration file.
Example
Logging
Databot Process Logging
The location of the databot log is specified in the configuration file as log.file and the logging level is specified as log.level. Valid log level values are log4j log levels: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, ALL and OFF.
...
logging:
file: /tmp/databot.log
loggers:
- io.novaordis.databot: DEBUG
...
If the configuration file does not specify logging configuration, the default logging level is INFO and the default logging file is "databot.log", placed in the same directory as the output data file. This is part of the base logging configuration, shipped as $DATABOT_HOME/lib/log4j.xml.
The command line flag "-v", if specified, will modify logging behavior until the configuration file is parsed and the new logging configuration is applied.
Also see:
Garbage Collection Logging
Garbage collection activity in the Java Virtual Machine running the databot agent is logged by default. The log file, named datebot-gc.log, is placed in the same directory as the data file. The startup script reads the YAML configuration file and infers the location of the directory, based on the output file configuration element content. If the output file is not specified in the YAML configuration file, the garbage collection log is written in /tmp.
Target-Specific Configuration Procedures
JBoss
In-Line Help
databot --help
Metric Reference
Troubleshooting
DataBot can be configured to provide TRACE-level logging information by setting the "io.novaordis" logger to TRACE level in the "logging:" section of the configuration file, as follows:
logging:
file: /tmp/databot.log
loggers:
- io.novaordis: TRACE
Note that this setting has has the side-effect of enabling TRACE logging on other libraries in use, some of which can be quite verbose. Netty is such a case. To turn off TRACE in other layers, use a configuration similar to:
logging:
file: /tmp/databot.log
loggers:
- io.novaordis: TRACE
- com: INFO
- org: INFO