Jenkins Docker Plugin: Difference between revisions
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
The image to be used as agent. Must be available in the local registry or into an accessible registry. | The image to be used as agent. Must be available in the local registry or into an accessible registry. | ||
Example: "jenkins-ssh-agent" as built by https://github.com/NovaOrdis/playground/blob/master/jenkins/docker/jenkins-ssh-agent/Dockerfile. | |||
====Connect Method==== | ====Connect Method==== | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 1 May 2018
External
- https://plugins.jenkins.io/docker-commons https://wiki.jenkins.io/display/JENKINS/Docker+Commons+Plugin
- https://plugins.jenkins.io/docker-plugin https://wiki.jenkins.io/display/JENKINS/Docker+Plugin
Internal
Overview
Docker plugin (ID docker-plugin) enables Jenkins to use a Docker server to provision build agents, run a single build and then tear down the agent. Optionally, the container can be committed after build. Docker plugin depends on Docker Commons plugin (ID docker-commons).
Concepts
Docker Agent
Docker plugin enables Jenkins to create dynamically and use for builds agents executing as containers within a Docker instance. Docker plugin requires that the agent containers are based on one of the following base images:
jenkins/ssh-slave
The image comes with sshd and a JDK. The Jenkins master will use ssh to connect into the agent's sshd. A SSH key based on unique Jenkins master instance identity can be injected in container on startup, obviating the need for password.
The image to be used as base is "jenkinsci/ssh-slave".
jenkins/jnlp-slave
The image comes with JDK. Jenkins master URL has to be reachable from the agent's container. The container will be configured automatically with the agent's name and secret. No special configuration of the container is needed.
jenkins/slave
An "attached" agent.
Installation
Plugin Installation
Manually from the UI or:
/usr/local/bin/install-plugins.sh docker-plugin
After the plugin is installed, a new configuration category shows up: Manage Jenkins -> Configure System -> Cloud. The installation process will also pull plugin dependencies.
Jenkins Server Configuration
Jenkins -> Manage Jenkins -> Configure System -> Cloud -> Add a new cloud -> Docker
Name
docker
The name should be something suggestive that indicates what docker server is actually used (ex: "Local SWMBP1 Docker Server").
Docker Host URI
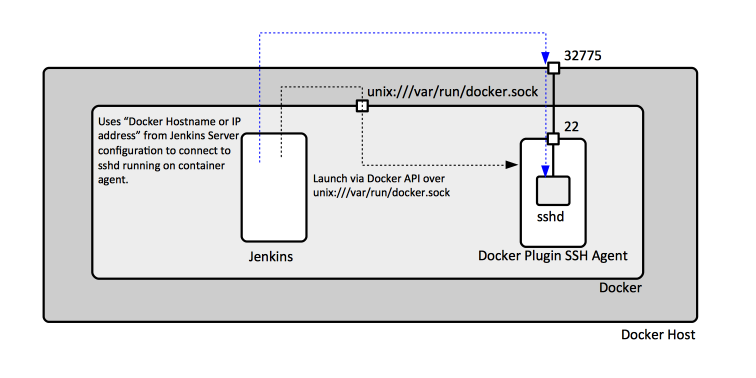
It is the URI to the Docker Host. May be left blank to use the default value defined by DOCKER_HOST environment variable. A typical value is unix:///var/run/docker.sock or tcp://127.0.0.1:2376.
Using Unix-domain Sockets for Jenkins Running as a Container
Note that if Jenkins itself runs as a Docker container on the same Docker server to be used for agent provisioning, and wants to use a Unix-doman socket for access, it won't have access by default to unix:///var/run/docker.sock of the Docker host. Access can be enabled by starting the Jenkins container as follows:
docker run ... --mount type=bind,source=/var/run/docker.sock,target=/var/run/docker.sock ... <jenkins-image>
This command maps the Docker-host level /var/run/docker.sock into the container with a bind mount, and sets appropriate permissions on the container-level /var/run/docker.sock so Jenkins can access it. Also, the Docker host-level user mapped to the Jenkins process must be added to the "docker" group, so it has access to the Unix socket. For more details see Non-root Management Access for Docker.
Jenkins container /var/run/docker.sock permissions:
ls -al /var/run/docker.sock
srw-rw---- 1 root jenkins 0 Apr 23 17:30 /var/run/docker.sock
Docker host /var/run/docker.sock permissions.
ls -al /var/run/docker.sock
srw-rw---- 1 root serviceusergroup 0 Apr 19 16:38 /var/run/docker.sock
Server credentials
Unix-domain socket do not require credentials, though the socket must have proper access permissions.
Advanced
Docker Hostname or IP address
Important: When using unix:///var/run/docker.sock as Docker host URI, it is important to provide a value here. This value will be used by Jenkins when attempting to connect to ssdd-running Docker agents, presumably deployed within the Docker server, which expose their sshd port on the IP address Docker server binds to. If the Jenkins server runs as a container in a Docker server, and it connects to a dedicated user-defined bridge network, Docker-based Jenkins agents may use automatic DNS resolution between containers when connecting to the Jenkins server: we can use the Jenkins master container name here.
Test Connection
Useful for debugging. A successful connection to the Docker server should return something like:
Version = 18.03.0-ce, API Version = 1.37
Enabled
Must be specifically enabled. Not by default.
Container Cap
The maximum number of containers that this provider is allowed to run in total. Note that containers that have not been created by Jenkins are counted as well. 0 disables provisioning of containers altogether. To get unlimited containers, use a non-reachable high value.
Docker Agent Templates
This section configures the images to be launched as agent container.
Labels
Each agent image is associated with a Jenkins label. The image must be available in an accessible registry.
Label example: "jenkins-ssh-agent-label"
Enables
Must explicitly enable.
Docker Image
The image to be used as agent. Must be available in the local registry or into an accessible registry.
Example: "jenkins-ssh-agent" as built by https://github.com/NovaOrdis/playground/blob/master/jenkins/docker/jenkins-ssh-agent/Dockerfile.
Connect Method
"Attach Docker Container", "Connect with JNLP", "Connect with SSH". Corresponds to one of the agent types (jenkins/slave, jenkins/jnlp-slave and jenkins/ssh-slave) and it must be in sync with the image declared as "Docker Image" above.
Tested with SSH, and it works.
Job Configuration
General -> "Restrict where this project can be run": use the label defined above.
Configuration
The agent images need to be created and accessible to the Jenkins server.