Java NIO and TCP Connections: Difference between revisions
(→Server) |
(→Server) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
while(true) { | while(true) { | ||
// | |||
// This call blocks until at least one I/O event occurs | |||
// | |||
selector.select(); | |||
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); | |||
for(Iterator<SelectionKey> i = selectedKeys.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { | |||
// | |||
// Figure out what kind of I/O event was selected | |||
// | |||
SelectionKey k = i.next(); | |||
if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) { | |||
// | |||
// New connection | |||
// | |||
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": new connection"); | |||
// | |||
// Remove the key from the set | |||
// | |||
i.remove(); | |||
// | |||
// Retrieve the SocketChannel for the new connection, make it non-blocking, and register | |||
// it with the same selector so now we can handle incoming data events on the same event | |||
// loop | |||
// | |||
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel)k.channel(); | |||
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); | |||
sc.configureBlocking(false); | |||
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); | |||
// | |||
// TODO this is where we pass the channel to a console subsystem to send data back on it | |||
// | |||
} | |||
else if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ) { | |||
// | |||
// New data available, read it | |||
// | |||
// | |||
// Remove the key from the set | |||
// | |||
i.remove(); | |||
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)k.channel(); | |||
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); | |||
int bytesRead = sc.read(buffer); | |||
if (bytesRead == -1) { | |||
// | |||
// TCP connection was closed | |||
// | |||
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": TCP connection closed"); | |||
// | |||
// Unregister the channel, by canceling the key. If we don't do this, data availability | |||
// events for zero-length data will keep popping up. | |||
// | |||
k.cancel(); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
// | |||
// Read data | |||
// | |||
buffer.flip(); | |||
byte[] content = new byte[bytesRead]; | |||
buffer.get(content, 0, bytesRead); | |||
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": " + new String(content)); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 25 July 2018
Internal
Overview
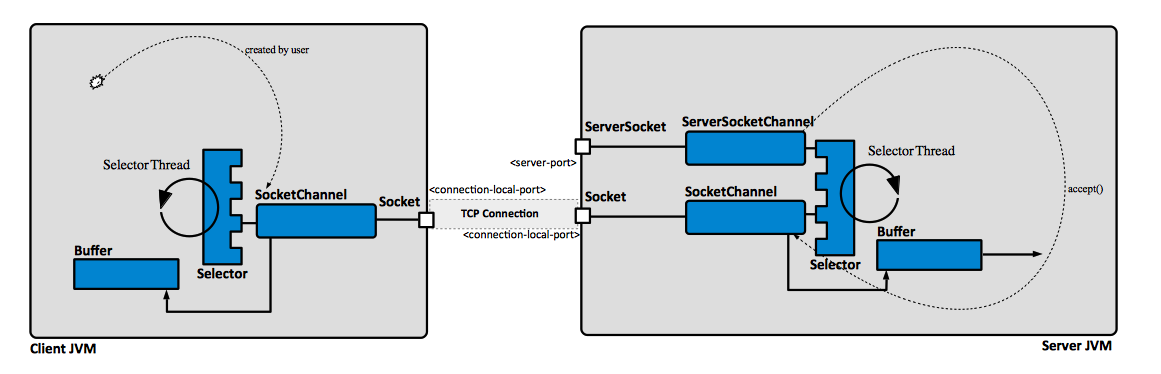
This article describes the programming model involved in establishing a simple TCP connection and interacting with it with non-blocking I/O, from Java. We use Java NIO APIs primitives introduced in Java 4.
Programming Model
Server
The server code uses a Selector to multiplex over selectable channels: selectable channels: a ServerSocketChannel that listens for incoming network connections and creates new SocketChannels for each new TCP connection, and subsequently registered SocketChannels.
//
// Main selector multiplexor. We use the main thread as selector thread.
//
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//
// The ServerSocketChannel used to accept new TCP connections
//
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(PORT);
ServerSocket ss = serverSocketChannel.socket();
ss.bind(address);
//
// Register the ServerSocketChannel with the selector
//
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
The main event loop handles two types of events: new connections and data availability on the existing connections. Once a new connection is detected, the selector thread retrieves the corresponding SocketChannel and registers it with the same selector. If data becomes available on any of the registered SocketChannels, we use a Buffer to read it.
//
// The main event loop
//
while(true) {
//
// This call blocks until at least one I/O event occurs
//
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for(Iterator<SelectionKey> i = selectedKeys.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
//
// Figure out what kind of I/O event was selected
//
SelectionKey k = i.next();
if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) {
//
// New connection
//
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": new connection");
//
// Remove the key from the set
//
i.remove();
//
// Retrieve the SocketChannel for the new connection, make it non-blocking, and register
// it with the same selector so now we can handle incoming data events on the same event
// loop
//
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel)k.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//
// TODO this is where we pass the channel to a console subsystem to send data back on it
//
}
else if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ) {
//
// New data available, read it
//
//
// Remove the key from the set
//
i.remove();
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)k.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = sc.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
//
// TCP connection was closed
//
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": TCP connection closed");
//
// Unregister the channel, by canceling the key. If we don't do this, data availability
// events for zero-length data will keep popping up.
//
k.cancel();
}
else {
//
// Read data
//
buffer.flip();
byte[] content = new byte[bytesRead];
buffer.get(content, 0, bytesRead);
c.info(TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.format(new Date()) + ": " + new String(content));
}
}
}
}