OpenAPI Specification: Difference between revisions
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
{{External|[https://swagger.io/specification/#responseObject Response Object]}} | {{External|[https://swagger.io/specification/#responseObject Response Object]}} | ||
200: | |||
description: 200 response | |||
headers: | |||
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: | |||
type: "string" | |||
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: | |||
type: "string" | |||
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: | |||
type: "string" | |||
responseSchema: | |||
$ref: '#/definitions/Empty' | |||
originalRef: '#/definitions/Empty' | |||
schema: | |||
$ref: '#/definitions/Empty' | |||
originalRef: '#/definitions/Empty' | |||
=Reference Object= | =Reference Object= | ||
Revision as of 23:37, 28 March 2019
Internal
Overview
The document addresses both OpenAPI 2.0 and OpenAPI 3.0. The differences will be emphasized.
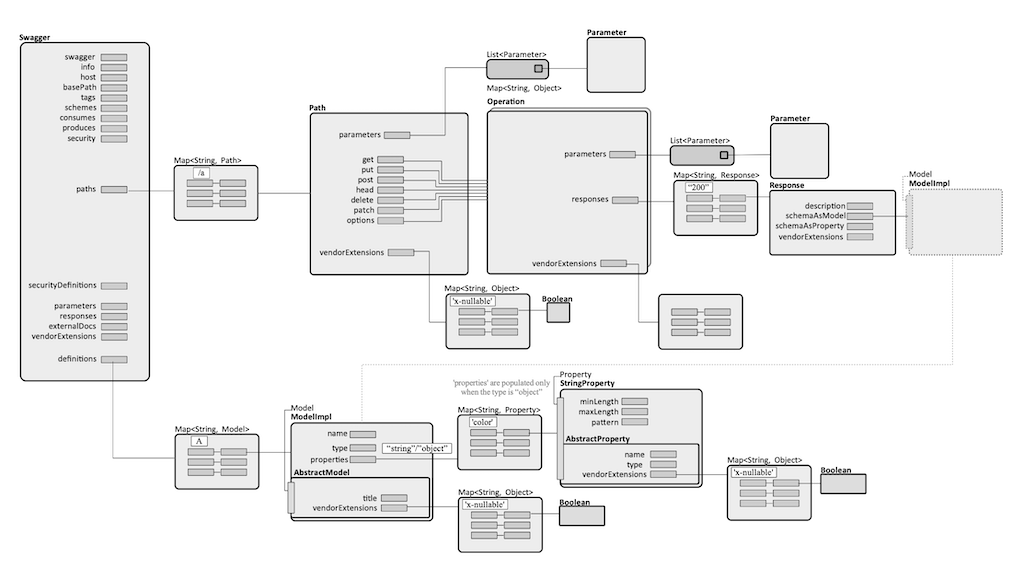
Swagger Java Model
info
title
When imported in AWS API Gateway, the title provides the API name.
paths
Contains a map of paths.
Path
The path is designated by its literal, as key in the paths map. Each path contains zero or one of these operations: GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS, a list of Parameters and a map of vendor extensions.
Operation
Also see:
responses
A required element that list all possible responses that are returned from executing this operations. The element must contain at least one response code. The container maps a HTTP response code to the expected response. The definition is not expected to cover all possible HTTP response codes, because they may not be known in advance. However, the definition should cover a successful operation response and any known errors. The "default" map key may be used as a default response object for all HTTP codes that are not covered individually in the definition.
paths:
/a:
get:
responses:
200:
...
default:
...
tags
Each API operation can be annotated with a list of tags. Tagged operations may be handled differently by tools and libraries. Optionally, each tag can get a "description" and an "externalDocs" in the global "tags" section on the root level. The tag names here should match those used in operations. The tag order in the global tags section also controls the default sorting in the UI - at least, for Swagger UI. It is possible to use a tag at operation level even if it is not specified on the root level.
tags:
-name: tag-a
description: Something that would shed light on tag-a semantics
externalDocs:
url: http://example.com/my-docs/tag-a.html
paths:
/a:
get:
tags:
- tag-a
- other-tag
Parameter
Response
200:
description: 200 response
headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Methods:
type: "string"
Access-Control-Allow-Headers:
type: "string"
responseSchema:
$ref: '#/definitions/Empty'
originalRef: '#/definitions/Empty'
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/Empty'
originalRef: '#/definitions/Empty'
Reference Object
CORS
More:
Organizatorium
x-nullable
Appears in automatically generated Swagger files, as such:
definitions:
LibraryAccount:
type: object
required:
- name
properties:
name:
type: string
x-nullable: true
definitions:
A:
type: string
title: A
x-nullable: true
When used for an API Gateway import, it errors out as:
Unable to create model for 'LibraryAccount': Invalid model specified: Validation Result: warnings : [], errors : [Invalid model schema specified. Unsupported keyword(s): ["x-nullable"]]