OpenShift DaemonSet Concepts: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
... | ... | ||
Note that internally, the declared pod template’s label selector must match the label selector above. | Note that internally, the declared pod template’s label selector [[OpenShift DaemonSet Definition#template_metadata_labels|must match the label selector above]]. | ||
When a pod is managed by a DaemonSet, the node the pod is scheduled to run on is selected by the DaemonSet, so the [[OpenShift Concepts#Scheduler|scheduler]] ignores it. The "unschedulable" field of a node is not respected by the DaemonSet controller. Also, the DaemonSet controller can make pods even if the scheduler has not been started, and this helps with cluster bootstrap. The DaemonSet chooses the nodes to run its pods on based on the [[OpenShift Concepts#Node_Selector|node selector]] specified in its definition: | When a pod is managed by a DaemonSet, the node the pod is scheduled to run on is selected by the DaemonSet, so the [[OpenShift Concepts#Scheduler|scheduler]] ignores it. The "unschedulable" field of a node is not respected by the DaemonSet controller. Also, the DaemonSet controller can make pods even if the scheduler has not been started, and this helps with cluster bootstrap. The DaemonSet chooses the nodes to run its pods on based on the [[OpenShift Concepts#Node_Selector|node selector]] specified in its definition: | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 9 February 2018
External
- https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/latest/dev_guide/daemonsets.html
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/daemonset/
Internal
Overview
A DaemonSet is a project-scoped OpenShift component that creates its associated pods and ensures they run on all (or some) nodes of a cluster. It is one of the pod controller types available in OpenShift.
If a node is added to the cluster, the DaemonSet insures that its associated pod will be scheduled on that node. When nodes are removed, the associated pods are shut down. Typical uses for DaemonSets are to run log collection agents (fluentd, logstash), node monitoring agents (collectd) or a cluster storage daemon (glusterd, ceph). Usually, a DaemonSet is needed for each type of daemon.
Example of DaemonSet definition:
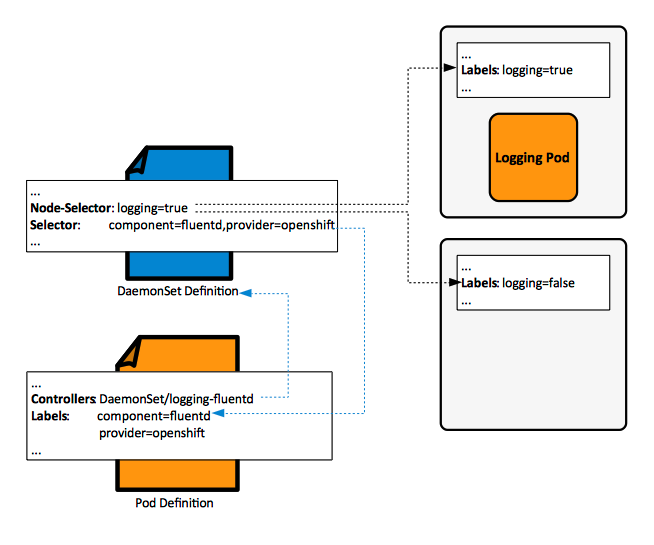
The DaemonSet decides whether it manages a pod or not based on the label selector expression specified in its definition:
...
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
component: fluentd
provider: openshift
...
Note that internally, the declared pod template’s label selector must match the label selector above.
When a pod is managed by a DaemonSet, the node the pod is scheduled to run on is selected by the DaemonSet, so the scheduler ignores it. The "unschedulable" field of a node is not respected by the DaemonSet controller. Also, the DaemonSet controller can make pods even if the scheduler has not been started, and this helps with cluster bootstrap. The DaemonSet chooses the nodes to run its pods on based on the node selector specified in its definition:
... Node-Selector: logging=true ...
After a successful placement, the node selector expression is recorded in the pod's definition.