Amazon EKS Create and Delete Cluster: Difference between revisions
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
==Test Access== | ==Test Access== | ||
At this point there are no nodes, but the cluster should be available. You can set up a "creator" context as described here, using the same IAM User identity (not a role): [[Amazon_EKS_Operations#Connect_to_an_EKS_Cluster_with_kubectl|Connect to an EKS Cluster with kubectl]]. | At this point there are no nodes, but the cluster should be available. It should be visible in the response of: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> | |||
aws eks list-clusters | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
You can set up a "creator" context as described here, using the same IAM User identity (not a role): [[Amazon_EKS_Operations#Connect_to_an_EKS_Cluster_with_kubectl|Connect to an EKS Cluster with kubectl]]. | |||
To set up access with an IAM role, worker nodes must be added to the cluster, otherwise the [[Amazon_EKS_Concepts#aws-auth_ConfigMap|aws-auth ConfigMap]] is not created. | To set up access with an IAM role, worker nodes must be added to the cluster, otherwise the [[Amazon_EKS_Concepts#aws-auth_ConfigMap|aws-auth ConfigMap]] is not created. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:41, 10 January 2022
External
Internal
Creation Procedure
This procedure documents creation from the AWS Console.
Create Resources
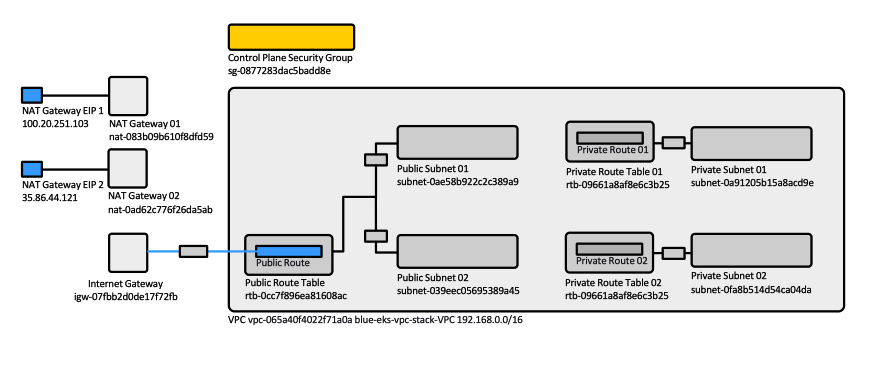
Create a dedicated VPC and associated resources using the pre-defined CloudFormation stack as described here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/getting-started-console.html, "To create your cluster" section. Use the latest template URL, not the one below:
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--region us-west-2 \
--stack-name blue-eks-vpc-stack \
--template-url https://amazon-eks.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation/2020-10-29/amazon-eks-vpc-private-subnets.yaml
For a list of all the resources created, open the AWS CloudFormation console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation and choose the blue-eks-vpc-stack stack and then choose the Resources tab. It does create:
- The VPC
- VPC Gateway Attachment
- Public route table
- Public route
- One internet gateway
- The control plane security group
- 2 x (private subnet, private route table, etc.)
- 2 x (public subnet, public route table, etc.)
- Use "public and private subnets" option.
- Do not specify an IAM role.
Write down the name of the stack, as it may be needed to delete the resources.
Also write down VpcId, SecurityGroups, SubnetId
Create the Cluster Service Role
For an explanation of what a cluster service role is see:
Creation
IAM console → Create role → AWS Service → Select a service to view its use cases → EKS → Select your use case → EKS Cluster → Next: Permissions (by default AmazonEKSClusterPolicy is selected) → Next: Tags
Role name:
<cluster-name>-service-role
Reuse from an Existing Cluster
Cluster → Configuration → Details → "Cluster IAM Role ARN"
Create the Cluster
Cluster Configuration
The cluster will be accessible to the IAM User that creates it without any additional configuration. Other users can be added as described in the Allowing Additional Users to Access the EKS Cluster section, after the cluster is created.
Create the cluster.
From the Console → EKS → Create Cluster
Name: ...
Cluster Service Role: the role created above, <cluster-name>-service-role.
Secrets Encryption
Disabled.
Tags
Optional.
Next.
Networking
VPC
Subnets (all existing subnets in the VPC are preselected).
If you intend to deploy LoadBalancer services that should be available externally, you must select at least one public subnet, otherwise you will get this upon LoadBalancer deployment: "Error syncing load balancer: failed to ensure load balancer: could not find any suitable subnets for creating the ELB"
Security groups
The security groups to apply to the EKS-managed Elastic Network Interfaces that are created in the worker node subnets.
The security group provided here are additional security groups.
The value can be left empty. Can it be updated later?
The cluster security group is created automatically during the cluster creation process. If nodes inside the VPC need access to the API server, add an inbound rule for HTTPS and the VPC CIDR block.
More concepts around EKS security groups and more details are available here:
Choose cluster IP address family
IPv4
Configure Kubernetes Service IP address range
OFF
Cluster endpoint access
This configures access to the Kubernetes API server endpoint.
Public and private.
If the endpoint access is public, sources to the public endpoint can be filtered by CIDR block.
Networking add-ons
Amazon VPC CNI
v1.10.1-eksbuild.1
CoreDNS
v1.8.4-eksbuild.1
kube-proxy
v1.21.2-eksbuild.2
Next.
Configure logging
Control Plane Logging
All disabled.
Next.
Create.
Test Access
At this point there are no nodes, but the cluster should be available. It should be visible in the response of:
aws eks list-clusters
You can set up a "creator" context as described here, using the same IAM User identity (not a role): Connect to an EKS Cluster with kubectl.
To set up access with an IAM role, worker nodes must be added to the cluster, otherwise the aws-auth ConfigMap is not created.
Provision Compute Nodes
Create a Compute IAM Role
Create a "compute" Role. Go to IAM, create role and:
AWS Services → EC2 → EC2 → Next: Permissions → Add AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy, AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy, AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly policies)
Name:
<cluster-name>-compute-role
Create Node Group
Select the EKS cluster, go to the Configuration tab, then Compute tab.
Add Node Group.
Name <cluster-name>-node-group[-postfix] (postfix could be memory "-128" or anything relevant). If only one node group is sufficient, call it <cluster-name>-default-node-group.
Node IAM role - the one created previously: <cluster-name>-compute-role.
Kubernetes labels. You can add labels now so pods can be scheduled based on them. Example:
Key: node-group, Value: <cluster-name>-node-group-128.
Next.
AMI type: Amazon Linux 2
Capacity type: On-Demand
Instance type: t3.2xlarge
Disk size: 20. If planning to use if for large images, etc. increase this. 60 GB.
Minimus size: 3 Maximu size: 3 Desired size: 3
Next
Select only the private subnets. Even if we will deploy public load balancers, they will work fine as long as the cluster was created with at least one public subnet.
SSH Key Pair - this gives access to the nodes.
Allow remote access from: All
Create.
kubectl get nodes
Other matters:
- If you plan to use NFS, make sure the security groups allow NFS inbound.
Scale-Up Node Group
Configure Access
Deletion Procedure
Delete Nodes and Cluster
Delete Nodes
Go to the cluster → Compute → Node Groups → Select → Delete.
Deleting the Node Group automatically terminates and deletes the instances.
Delete the Cluster
Delete the cluster.
Delete the Associated Resources
Remove the associated resources (subnets, VPC, etc.) by running Delete on the CloudFormation stack used to create resources.