Gradle Concepts
External
- DSL reference https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/
Internal
Overview
Gradle is a general-purpose build tool, which can build pretty much anything its configuration scripts declare. It is primarily used to build Java and Groovy, but it can build other languages as well.
Configuration Scripts
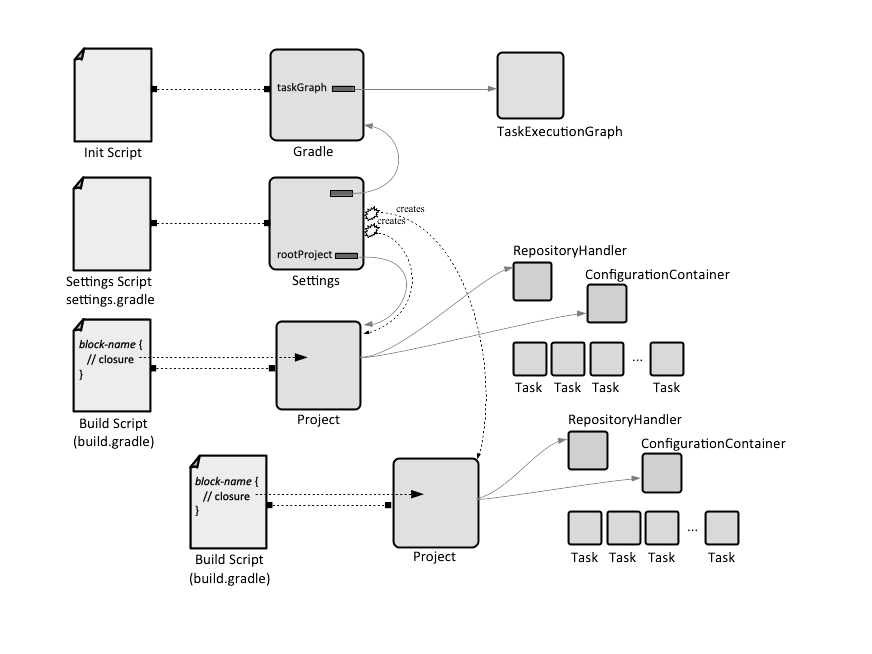
The configuration scripts are written in the Gradle build language, which is a DSL and a Groovy extension. A build is configured by three types of configuration scripts, which together express build requirements and inform the build runtime: build scripts, a settings script and an init script. Each of those scripts contains executable statements and script blocks, which are a special case of executable statement, consisting in a method invocation on a closure. The logic expressed in a specific script applies to its delegate object. Though syntax is similar for all three scripts, specific blocks must make sense with the delegate object. The corresponding delegate objects for all three types of configuration scripts will be described below.
A configuration script may contain statements and script blocks. A statement may be a method call, property assignment and local variable definition. A script block is method call that takes a configuration closure as an argument. Executing the script block results in modification of the associated delegate object, based on the content of the closure. Each configuration script implements the Script interface, which exposes a number of useful methods and properties.
Settings Script
Build Script
Init Script
Build Lifecycle
- Core Types:
- Settings. https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/org.gradle.api.initialization.Settings.html
- Project. https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/org.gradle.api.Project.html
- Gradle. https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/org.gradle.api.invocation.Gradle.html
- Task https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/org.gradle.api.Task.html
- Configuration https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/org.gradle.api.artifacts.Configuration.html
- A build consists of executing a series of tasks in succession.
- Extensions, as in publishing extension.
- Go through the lifecycle without plugins. Understand. Then introduce essential plugins.
- Most of Gradle's power comes from external plugins
- Java plugin.
- Maven publishing plugin.