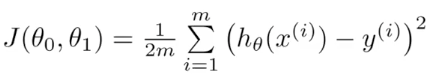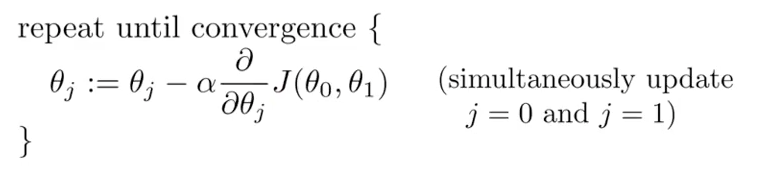Machine Learning
Internal
Machine Learning
The science of getting computers to learn without being explicitly programmed (Arthur Samuel).
A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E (Tom Mitchell)
Neural Networks
Learning algorithms that mimic how the brain works.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Learning Algorithms
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, we have at our disposal a dataset that tell us which is the "correct answer".
Input variables, output (target) variables.
A pair of one input variable and one output variable is called a training example.
The dataset is called a training set.
Definition: given a training set, learn a function h: X -> Y so that h(x) is a "good" predictor for the corresponding value of y. For historical reason, this function is called hypothesis. The learning algorithm outputs a function (h - hypothesis). The hypothesis function maps input variables to output variables. When the target variable we're trying to predict is continuous, the learning problem is a regression problem. When the target variable can only take a number of discrete values, we call the problem a classification problem.
The accuracy of the hypothesis is measured by a cost function. A common cost function is the squared error function or mean squared error.
We are trying to minimize the cost function.
Gradient descent is an algorithm to minimize the cost function (and other functions). Local minimum (local optimum). Alpha is the learning rate.
"Batch" gradient descent - the algorithm uses the entire training set.
Gradient descent is iterative.
Regression Problem
The goal is to predict a continuous value.
See:
Classification Problem
A classification problem is the problem of identifying which category (out of a set of categories) an example belongs to. The goal of a classification problem is to predict a discrete value out of a set of possible discrete values.
See:
Unsupervised Learning
- Clustering problems.
Reinforcement Learning
Recommender System
Feature
Synonymous with attribute.
Also input
Infinite number of features.
Feature vector.
Parameters
Theta