OpenShift Security Concepts
External
Internal
User
Interaction with OpenShift is associated with a user. An OpenShift user is an entity that can make requests to the OpenShift API. Typically, an user represents the account of a developer or administrator. The users are internally represented with an User object, which in turn represents an actor. Permissions can be given to actors in the system by adding roles to them, or their groups. The association between an user or group and a role is called binding. A user/group may be bound to multiple roles.
There are several user types:
Regular User
Regular users are created upon login or via the API.
System User
Most system users are created automatically when the infrastructure is defined, for the purpose of enabling the infrastructure to interact with the API securely. System users include:
The Cluster Administrator
The cluster administrator has access to everything.
"system:admin"
Per-Node User
Service Account
Special system, non-human users that act automatically with designated access to objects in their projects or other projects. Typically used by services such as routers and registries, or when system components need to make an API call to the master. Service accounts are created automatically when a new project is created, and the content of "serviceAccountConfig/managedNames" in the master configuration file specify what service accounts to be created. By default, "builder", "deployer" and "default" are created for all projects. Service accounts provide a way to control API access without sharing regular user credentials. Service account authenticated to the API using tokens signed by an internal private RSA key, which is verified by the authentication layer. Service accounts can be granted roles like a regular user, using oc policy add-role-to-user command. Every service account is member of the groups "system:service accounts" and "system:serviceaccounts:<project>" and it is given the "system:image-puller" role. The service accounts are represented with the ServiceAccount object. Examples: "system:service account:default:deployer".
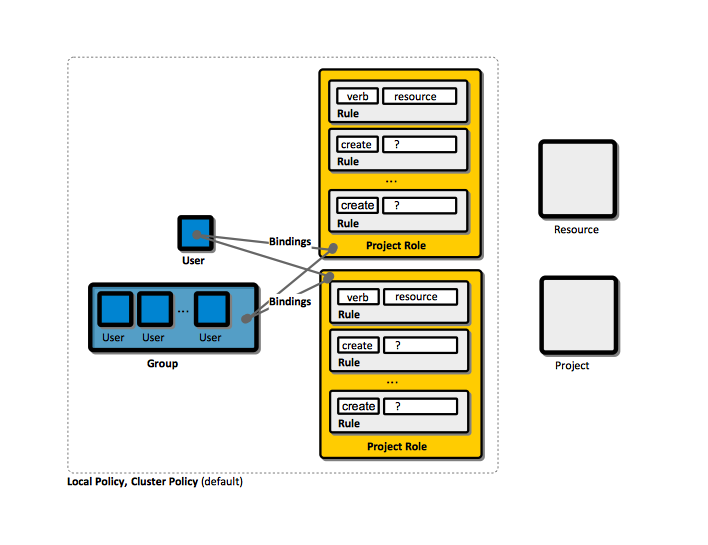
Group
Binding
Role
Rule
Relationship between Users, Groups, Bindings, Roles and Rules
Policy
Authentication
The authentication layer provides a framework for collaboration and quota management. It supports multiple mechanisms for authentication. API calls are authenticated with a token issued by the authentication mechanism. The authentication is performed with oc login.
Authentication Methods
Identity Providers
Authorization
Security Context Constraints
OpenShift uses Security Context Constraints (SCCs) to control the actions that a pod can perform and what it has the ability to access.