Gradle Concepts
External
- API reference https://docs.gradle.org/current/javadoc/index.html
- DSL reference https://docs.gradle.org/current/dsl/
Internal
Overview
Gradle is a general-purpose build tool. It is primarily used to build Java and Groovy, but it can build other languages as well. The goal of a Gradle execution, also known as a Gradle build, is to execute a set of tasks, in a desired sequence. The sequence in which tasks are executed is determined based on the dependencies declared between tasks. Gradle guarantees that the tasks are executed in the order of their dependencies, and each task is executed only once. This behavior is achieved by building a task directed acyclic graph, before any task is executed.
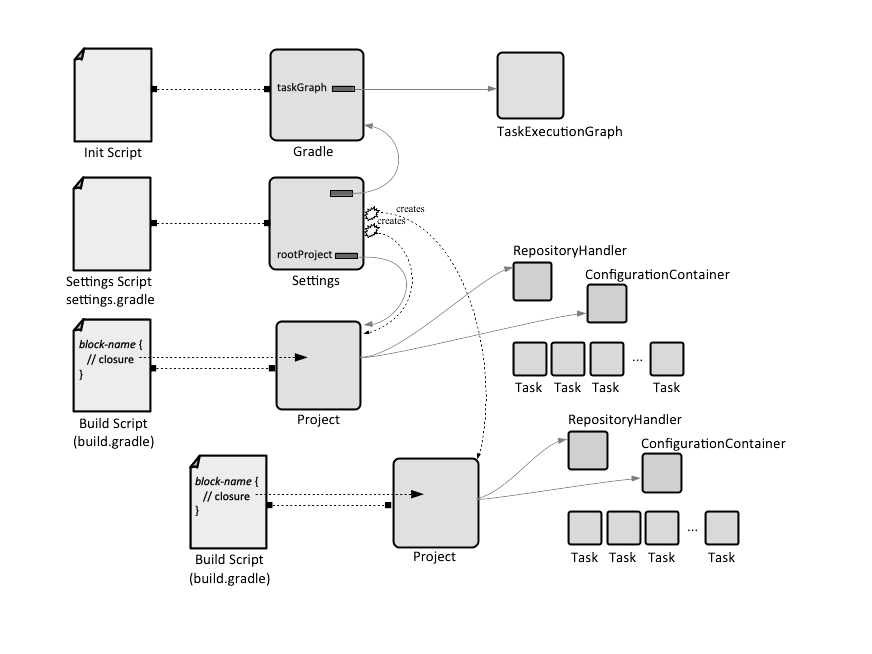
Each build runs according to a well defined build lifecycle, during which Gradle instantiates a complex domain model of the project in memory: a Gradle instance, a Settings instance and the project itself.
Build Lifecycle
A build is a Gradle execution. Each build starts with instantiation of a Settings and Gradle instance, then of at least one project, which in turn contains tasks, and it can be configured and controlled with properties. Depending on the specific of the build, other Gradle core types are instantiated as well. The lifecycle of a Gradle build consists in an initialization, configuration and an execution phase. Code can be written to react to a build's lifecycle events.
Initialization Phase
The build starts with the initialization phase. Gradle creates a Gradle instance and a Settings instance, then executes the settings script, which can be used to update the state of its Settings delegate. In case of a simple project, Gradle creates the Project instance. For a multi-project build, and depending on which project is executed, Gradle figures out which of the project dependencies need to participate in the build. It creates a project representation for each of the projects, defining the build's project hierarchy. The sub-projects are declared using the "include" or "includeFlat" Settings methods in settings.gradle. Note that at the initialization phase, Project instances are not accessible from the settings script. Project data can be accessed, and some of it mutated, via a ProjectDescriptor interface instead. Extra properties for Gradle and Settings object instances can be declared at this phase. None of the build scripts is executed in this phase.
Configuration Phase
The code declared in build.gradle is executed in order in which it was declare, against the root project instance and its sub-projects. The order in which Project instances is configured is determined ? The plugins declared in the build scripts are downloaded and initialized in their corresponding Project instances. According to the configuration on demand principle, only relevant projects are configured. Tasks are instantiated and configured, by executing their configuration closures. Any configuration code is executed with every build of the project. Gradle constructs a task DAG. The incremental build features determines if any of the tasks in the model are required to run.
Execution Phase
The execution phase requires that one or more tasks is specified on command line. Task actions are executed in the correct order, as determined by their dependencies. Task considered up-to-date are skipped and a a task is executed only once.
Configuration Scripts
Syntax
The configuration scripts are written in the Gradle build language, which is a Groovy extension DSL. Each configuration script (init.gradle, settings.gradle and build.gradle) implement the Script interface. The script contain statements, script blocks and any elements allowed in a Groovy script, such as method and class definitions. The script elements are executed in the order in which they are declared in the script and they apply to the script's delegate object. Though syntax is similar for all three scripts, specific blocks must make sense with the delegate object.
Statements
A statement may be a method call, property assignment and local variable definition.
println 'this will be sent to stdout'
If the script's delegate object has an accessor that follows Java Beans conventions, then the result of the accessor invocation can be obtained simply specifying the corresponding variable name. For example, the root project instance returned by:
public interface Settings ... {
ProjectDescriptor getRootProject();
}
can be accessed from the corresponding settings.gradle script with rootProject.
Script Blocks
A script block is a special case of an executable statement, consisting in a method invocation on a closure. Executing the script block results in modification of the associated delegate object, as specified in the closure. This is said to delegate the closure against the target object, or e executed the closure in scope of the class of the target instance. it is the default parameter passed to all Groovy closures. A build configuration that does not declare any plugin has a set of standard script blocks. Plugins may, and usually do, add new script blocks.
Available Scripts
Convention over Configuration
Subjects
- Project, Dependencies and Configurations, Multi-Project Builds, Reacting to Build Lifecycle Events, ProjectDescriptor
- Task, Extending Gradle with a Custom Enhanced Task, Incremental Builds, Build Cache
- Gradle Properties - Runtime and Project Configuration
- Gradle Instance, Settings Instance
- Logging
- Plugins
- Extending Gradle
- Gradle File Resolution
- Configuration on Demand