Selenium Concepts
Internal
Overview
Selenium is a set of tools and libraries that can be used to automate testing of UI web applications running in browsers. Modern web browsers expose browser automation APIs that can be used to control the browser and run tests. Selenium operates on those APIs via its WebDriver component and it essentially remotely controls the browser, emulating a user's interaction with the browser: mouse movement, entering text into fields, selecting drop-down values, checking boxes and following links. As such, Selenium is at its core a browser user agent library. Selenium tests are expensive to run, but they have the advantage of being able to test all components of the application, from backend to frontend, from a user’s perspective.
Web Browser
Web browsers or user agents are the target of Selenium tests.
Browser Automation APIs
Modern browsers expose browser automation APIs that allow programmatically operating the browser as if a real user would do it. The availability of such API facilitate writing automated tests that simulate very closely a user interaction with the browser and with the application rendered by the browser. The Selenium component that interacts with the browser's automation API is WebDriver.
WebDriver
WebDriver is an API and a platform- and language-neutral wire protocol that defines an interface for controlling the behavior of web browsers (user agents). WebDriver takes the browser interaction mechanics to the browser vendor, asking it to take responsibility of the backend, browser-facing implementation. WebDriver is part of the W3C standardization process, with the goal of becoming the standard remote control library for user agents.
Driver
Each browser is backed by a specific WebDriver implementation called a driver. The driver handles the communication to and from Selenium and the browser.
Google Chrome Driver
Mozilla GeckoDriver
WebDriver APIs
WebDriver does not require its API to be compiled with the web application code, so it is not intrusive and allows testing the same application that is available in production.
WebDriver Protocol
WebDriver Test
Selenium IDE
The Selenium IDE is a tool that can be used to develop Selenium test cases. It is offered as Chrome and Firefox extensions. It records the user's actions in the browser and translates them into Selenium commands, producing Selenium scripts. The Selenium IDE can be extended through the use of plugins, which can introduce new commands to the IDE, or integrate with a third-party service.
IDE Plugins
Selenium Scripting
Selenium scripts can be produced by recording the user's actions in a browser via the Selenium IDE. During such a recording session, the IDE generates the appropriate Selenium commands with parameters defined by the context of the element being accessed.
Selenium Commands
Selenium Grid
Selenium Grid is a tool allowing to run tests cases in different machines across different platforms. The Grid facilitates running the same WebDriver test on multiple browser and operating system combinations.
Selenium Tests
A Selenium test consists of actions, performed from the user's point of view, within the context of pages in the site. There are several types of tests that can be automated with Selenium:
Functional Test
A functional test determines if a feature or system works properly. The test helps answering the question: "are we building the product right?"
Acceptance Test
An acceptance test establishes if a feature or a system meets the customer expectations and requirements. This type of test generally involves the customer's cooperation or feedback. It is a validation activity that answers the question: "are we building the right product?". An acceptance test is a subtype of a functional test.
Regression Test
Performance Test
Load Test
Load testing is done to verify how well the application works under different defined loads, usually a particular number of users connected at once.
Stress Test
Stress testing is done to verify how well the application works under stress, which means above the maximum supported load.
Organizatorium
Page Object Model
TO REFACTOR
Selenium Architecture
Selenium has a client-server architecture, and includes both client and server components.
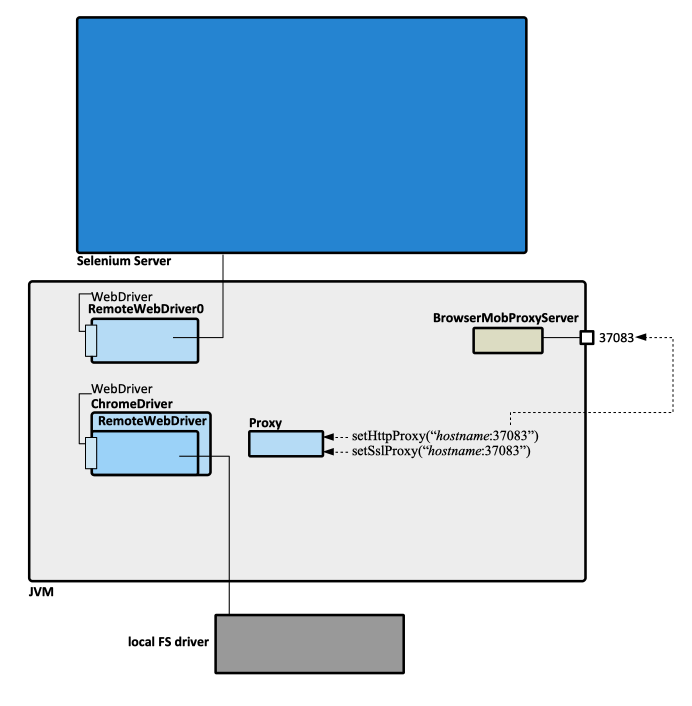
Client
The Selenium client exposes the WebDriver API, which can be used to interact with the page. The client extends RemoteWebDriver, which communicates with the remote Selenium server. There are browser-specific constructors for the WebDriver (ChromeDriver, FirefoxDriver). There is still confusion on whether the client loads and uses a local driver or connects remotely to a server.
Server
The Selenium server receives request from the Selenium client's RemoteWebDriver. It also includes WebDriver API to run tests against web browsers on the server machine.
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("http://example.com");