Amazon ECS Concepts: Difference between revisions
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
{{Internal|Amazon ECS Service Discovery Concepts|Service Discovery Concepts}} | {{Internal|Amazon ECS Service Discovery Concepts|Service Discovery Concepts}} | ||
=Launch Type= | =Launch Type= | ||
Revision as of 00:47, 8 February 2019
External
Internal
Overview
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) allows deploying Docker containers on a scalable cluster. Docker images to be deployed typically come from Amazon ECR.
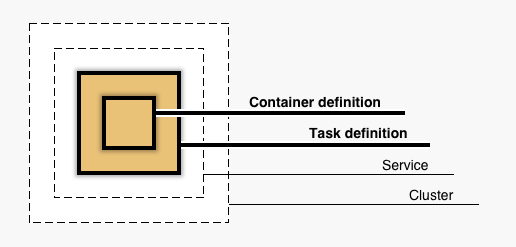
Container
The container is based on an image, that should be chosen when creating the container.
Cluster
An Amazon ECS cluster is a regional, logical grouping of tasks and services. If the tasks or services in question use the EC2 launch type, the cluster is also a grouping of container instances. A default cluster is always available, but multiple clusters can be created in an account to keep your resources separate. A cluster cannot span more than one region.
Relationship between a Cluster and a VPC
Cluster Configuration
Cluster Name
Cluster VPC
See above:
Cluster Subnets
Cluster Operations
Task
A task is a running instance of some runtime, usually a container. A running task listens on ports, generates logs, and hopefully does useful work. The running tasks is generated based on a task definition and is usually started by a service. However, a task can be manually run (Task Definitions -> Actions -> Run Task), where the cluster, the number of tasks, the VPC, the subnet, etc. need to be specified.
Running Task
A running task is based on a task definition and it has an unique ID (e.g. e822d0018c324c47a2001e8ea6a76d4f). The running task has associated time statistics, such as "Created at" and "Started at". Also, stdout content generated while the task is running is available as Cluster -> <cluster-name> -> Tasks -> <task-id> -> Logs. Every time the task is started, it gets a new Private IP, and if it was configured with one, a new Public IP.
A running task may be started by a service. When a task has been started by a service, it can be restarted (re-deployed) by navigating in console to the service, selecting the task, selecting the task in question and then "Stop"-ing it. A warning will pop up, saying that the task has been started by a service, but it can be safely stopped: the service will start a replacement.
Stopped Task
Task Definition
A task definition is a blueprint, or a configuration, for an application, and describes one or more containers through attributes. Some attributes are configured at the task level but the majority of attributes are configured per container. It specifies the Docker image, how many containers to use for this task and the resource allocation for each container. To modify the task definition, a new revision must be created and then make the required changes to the task definition.
Task definitions exist outside clusters, and can be shared between clusters.
Task Definition Name
Network Mode
The Docker networking mode to use for the container in the task. A typical conventional value is "awsvpc".
Task Role
The task role is the IAM role that allows the containers in the task permission to call the AWS APIs that are specified in its associated policies on the IAM user's behalf. The steps necessary to create a Task Role, as well as specific individual permissions are described in detail in:
Task Execution Role
The task execution role is the IAM role that allows the containers in the task to pull container images and publish container logs to CloudWatch on the IAM user's behalf. The steps necessary to create a Task Role, as well as specific individual permissions are described in detail in:
Compatibilities
The launch type used by the task.
Task Memory
Task CPU
Task Revision
A new task revision is created when a task definition is modified.
Task Operations
Service
A service allows running and maintain a specified number (the "desired count") of simultaneous instances of a task, created based on a task definition, in an ECS cluster. The service launches and maintains running tasks in the cluster. It detects stopped tasks and starts new ones to maintain the number of tasks specified in the service definition. If the number of tasks exceeds 1, a load balancer is required to distribute incoming traffic amongst sibling tasks.
Unlike a task definition, a service only exists within a cluster, and cannot be shared between clusters. From this perspective, a service can be thought of as an instantiation context of a task, specifying the cluster, the VPC, subnet, security group, etc.
Service Definition
Generic
Service Name
Number of Desired Tasks
Service Type
It ca be REPLICA for a FARGATE launch, or REPLICA or DAEMON an EC2 launch.
Network
Cluster VPC
Security Group
A security group is created to allow all public traffic to the service only on the container port specified. Security groups and network access can be further refined after the service creation.
The name of the security group can be changed at this stage, as well as the port configuration.
Service Status
Service's Task Definition
Load Balancer Type
Service Operations
Service Discovery
Launch Type
EC2 Launch Type
The EC2 launch type allows running a containerized applications on a cluster of Amazon EC2 instances.
Fargate Launch Type
The Fargate launch type allows running a containerized application without the need to provision and manage the backend infrastructure. It only requires registering a task definition. When that is available, Fargate launches the container.