Events-api Concepts
Internal
Event
An event consists of a set of properties which describe the state of a system at the time the property values were read.
By default, an event is not associated with a specific moment in time. However, for most practical situations, the time when properties are read is important, and the instance of such an event is modeled by timed events.
An event's
Event Interface Refactoring Needed
TODO 9ys5C3 The current Event interface is flawed because it assumes that only one property with a certain name can exist. Data collection from multiple metric sources produced events that may contain multiple properties with the same name, but which refer to different readings. Reconcile this:
- Introduce "source" on Property? Not generic enough.
- Introduce a generic key instead of name on Property? Confusing.
- Keep the constraint that property only have names, and the names are unique, and model the situation presented above with creating a top-level event, whose properties have names inferred from the source name, and values the events generated by the sources themselves. This would be a hierarchical event, and probably we should introduce convenience API to assist with this situation? The downside is it's complicated.
Timed Event
A timed event is an event that has a timestamp. The values of all event's properties are read at the moment in time marked by the timestamp.
Property
A name/value pair with additional attributes, such as measure unit, presentation format, etc. The value usually represents the snapshot in time of a certain runtime value, so that is why the terms "property" and "reading" are interchangeably used.
Does the format belong here, or at a different level?
Metric
Metric Source
A source of metrics. Implies an underlying mechanism that can be used to obtain a set of values given a set of metric definitions, ideally in a single operation, for performance reasons. However, the implementations are free to define what "efficient reading" means. Example of metric sources:
- Local O/S instance can be queried for metrics such as free memory, CPU usage or disk space.
- Remote O/S instance can be queried for metrics such as free memory, CPU usage or disk space over a SSH connections (assuming credentials are available and the system is reachable).
- The JMX bus of a local or remote Java virtual machine.
- The management controller (standalone or domain) of a WildFly instance.
A metric source instance must be started before metrics can be collected from it. The start operation usually implies expensive remote connection creation, initial state verification, etc. so metric source implementations should be designed to be started once and then stay in that state indefinitely. However, the underlying connection may break for various reasons during the metric source life, so it may become necessary to re-start a metric source.
Implementations are NOT expected to maintain their own internal threads. The recommended way to manage sources and collect metrics is to do it with external threads/executors.
The implementations must correctly implement equals() and hashCode(), as metric sources will be used as map keys.
Metric Source Address
OS
Local OS
Remote OS
Valid addresses:
ssh://username@hostaddress:port
"ssh://" protocol implied:
username@hostaddress:port
JBoss Management Controller
jbosscli://admin@1.2.3.4:9999/
"jbosscli://" implied:
admin@1.2.3.4:9999/
The default value, if not specified, is "localhost:9999".
JMX Bus
jmx://admin:adminpasswd@1.2.3.4:2345
Classpath.
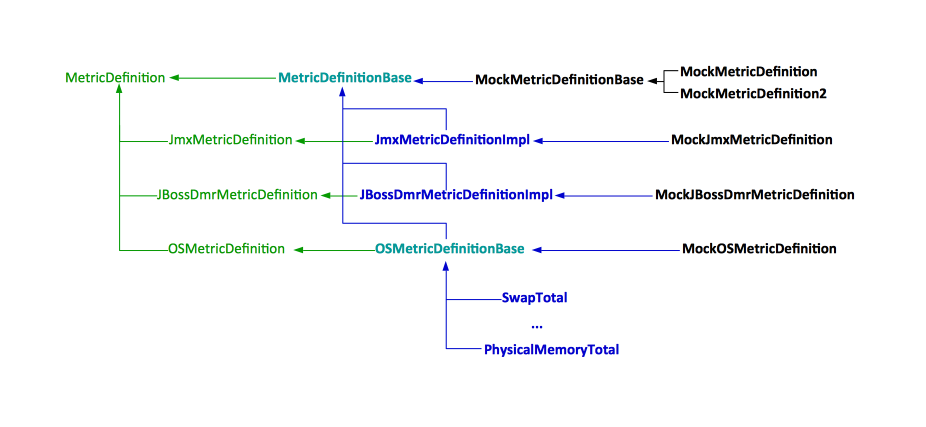
Metric Definition
A metric definition is an instance that contains all the information a metric source needs in order to extract a value (reading) for a specific metric.
Metric Definition ID
The metric definition has an ID which uniquely identifies the metric to a metric source. The ID must not include anything that ties that ID to a specific metric source. The same ID can be given to different metric sources, and each metric source will return a different value of the metric. For example, "PhysicalMemoryTotal" uniquely identifies the total physical memory metric in the context of a local or remote operating system instance, "java.lang:type=Threading.ThreadCount" uniquely identifies the JVM thread count metric in the context of a JVM's platform MBean server and "/subsystem=messaging/hornetq-server=default/jms-queue=DLQ:message-count" uniquely identifies the DLQ queue depth metric for a specific broker node, managed by a JBoss management controller.
Metric Source Address
A specific instance of a metric definition can be associated with a metric source via the metric source address.
Relationship between a Metric Definition and a Metric Source
A metric source receives a metric defintion and if the source recognizes the definitions, it returns a value (reading) associated with that definition, in form of a property instance:
List<Property> collectMetrics(List<MetricDefinition> metricDefinitions) throws MetricException;
The method collects all metrics whose definitions are given as argument. If a value corresponding to a specific metric definition from the list cannot be successfully collected, a Property instance with the correct id, type and base unit must is returned, but its value is null. Implementations may log as WARN more details on why the collection failed. Implementations may choose - and they are encouraged - to attempt to start the source in-line, if the source is not already started. They, however, may chose to signal the fact that the source is not started and request an external start. The metric source will throw an exception if if finds at least a metric definition that has a null or different source. This indicates a programming error, not a runtime collection failure.
A Property instance returned for a specific metric definition has its name equals with the metric definition ID.
OS Metric Defintion
Local:
PhysicalMemoryFree
Remote:
ssh://test-remote-host:22/PhysicalMemoryFree
JBoss CLI Metric Defintion
Default (implies the default local jboss instance):
/subsystem=messaging/hornetq-server=default/jms-queue=DLQ/message-count
Remote:
jbosscli://admin:adminpasswd@1.2.3.4:9999/subsystem=messaging/hornetq-server=default/jms-queue=DLQ/message-count
JMX Metric Defintion
jmx://admin:adminpasswd@1.2.3.4:2345/jboss.as:subsystem=messaging,hornetq-server=default,jms-queue=DLQ/messageCount