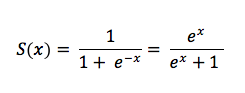Sigmoid Function: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "=Internal= * Mathematical Analysis") |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=External= | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sigmoid_function | |||
=Internal= | =Internal= | ||
* [[Mathematical_Analysis#Subjects|Mathematical Analysis]] | * [[Mathematical_Analysis#Subjects|Mathematical Analysis]] | ||
=Overview= | |||
Often, the sigmoid function refers to a special case of the [[#Logistic_Function|logistic function]]. | |||
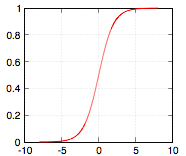
=Logistic Function= | |||
:[[Image:LogisticFunction.png]] | |||
:[[Image:LogisticFunctionGraph.png]] | |||
Used by: | |||
* [[Neural_Networks#Individual_Unit|Neural network units with logistic activation functions]]. | |||
==Logistic Function MATLAB Implementation== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang='MATLAB'> | |||
% | |||
% Compute the logistic function of z, where z can be a scalar, vector or matrix | |||
% | |||
function s = logistic(z) | |||
s = 1 ./ (1 + (e .^ (-1 .* z))); | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Latest revision as of 06:38, 4 January 2018
External
Internal
Overview
Often, the sigmoid function refers to a special case of the logistic function.
Logistic Function
Used by:
Logistic Function MATLAB Implementation
%
% Compute the logistic function of z, where z can be a scalar, vector or matrix
%
function s = logistic(z)
s = 1 ./ (1 + (e .^ (-1 .* z)));
end