KVM Virtual Networking Concepts: Difference between revisions
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
[[Image:RHELVirtualNetworking_NATMode.png]] | [[Image:RHELVirtualNetworking_NATMode.png]] | ||
The [[Network Address Translation (NAT)|network address translation]] function is implemented as [[Network_Address_Translation_(NAT)#IP_Masquerading|IP masquerading]], using [[Iptables_Concepts#nat|iptables]] rules. Connected guests will use the virtualization host physical machine IP address for communication with external networks (it is possible that the virtualization host IP address is unroutable as well, if the virtualization host sits in | The [[Network Address Translation (NAT)|network address translation]] function is implemented as [[Network_Address_Translation_(NAT)#IP_Masquerading|IP masquerading]], using [[Iptables_Concepts#nat|iptables]] rules. Connected guests will use the virtualization host physical machine IP address for communication with external networks (it is possible that the virtualization host IP address is unroutable as well, if the virtualization host sits in its own NAT domain). By default, without additional configuration, external hosts cannot initiate connections to the guest virtual machines. | ||
==Routed Mode== | ==Routed Mode== | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 27 June 2017
External
Internal
Overview
This article discusses concepts related to virtual networking with libvirt.
Virtual Network Switch
libvirt implements virtual networking using a virtual network switch. A virtual network switch is a software component that runs on the virtualization host. The virtual machine guests connect to it and the network traffic to and from the guests passes through the virtual switch.
The virtual switch is started and managed by the libvirtd daemon and is represented as the virbr0 network interface:
# ip addr
...
7: virbr0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:15:ef:87 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.122.1/24 brd 192.168.122.255 scope global virbr0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
...
The virtual network switch can operate in several modes, described below:
The DNS and DHCP Server
The virtual network switch uses a DNS and DHCP server. The DNS and DHCP are both served by a dnsmasq instance running on the virtualization host. The configuration file is /var/lib/libvirt/dnsmasq/default.conf, but the configuration file should not be edited manually, but with
virsh net-edit default
Virtual Network Modes
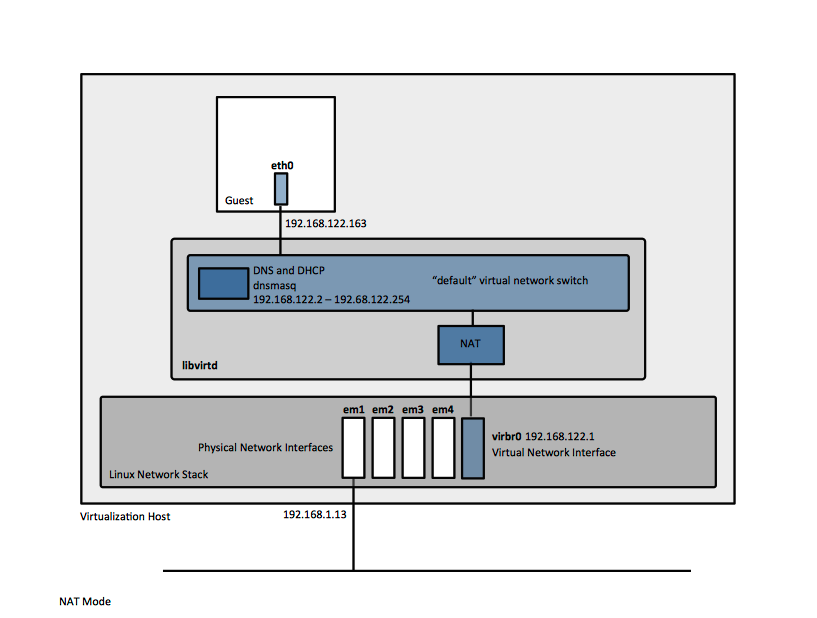
NAT Mode
The NAT mode is the default mode in which libvirt virtual network switch operates, without additional configuration.
The network address translation function is implemented as IP masquerading, using iptables rules. Connected guests will use the virtualization host physical machine IP address for communication with external networks (it is possible that the virtualization host IP address is unroutable as well, if the virtualization host sits in its own NAT domain). By default, without additional configuration, external hosts cannot initiate connections to the guest virtual machines.
Routed Mode
Bridged Mode
Isolated Mode
Organizatorium
A virtual machine guest that connects to an external network uses the software network components of the physical host, which are managed by libvirt's virtual network configuration. The host acts as a virtual network switch. By default, all guests on a single host are connected to the same virtual network, named "default". Guests have default direct IP connectivity to all other guests and to the host. libvirt network filtering and guest operating system iptables rules apply. Guests have external outbound access via NAT, subject to the host system's firewall rules. From the point of view of the guest operating system, a virtual network connection is the same as a normal physical network connection.
The guest network interfaces can be set to one of the following modes:
- isolated mode - the network won't allow any traffic beyond the virtualization host.
- routed mode - the network will route traffic between the guest and external hosts without performing any NAT. This enables incoming connections but requires extra routing table entries for the systems on the external network.
- bridged mode - the guests are connected to a bridge device that is also connected directly to a physical ethernet device connected to the local ethernet. This makes the quests directly visible on the physical network, and thus enables incoming connections, but does not require any extra routing table entries.