Iptables Concepts
Internal
Overview
iptables is cable of tracking a connection's state. For more details see How State Machine Connection Tracking Works.
iptables is specifically built to work on the headers of the Internet and the Transport layers. It is possible to do some very basic filtering Application and Network access layers as well, but iptables was not designed for this, nor is it very suitable for those purposes. iptables does not do string matching, because a specific string can be spread across several packets, and assembling data from different packets is too processor and memory intensive.
It's always a good idea to have an iptables configuration in place on a given machine, regardless of outside firewalls you may have. Each individual machine, depending on its uses, might have different packet filtering needs. As a result of this, the external firewall device should have a configuration that permits everything the most permissive of your local systems is going to need to do: each individual machine, then, can deny as much of that as it can get away with, without sacrificing its critical functionality.
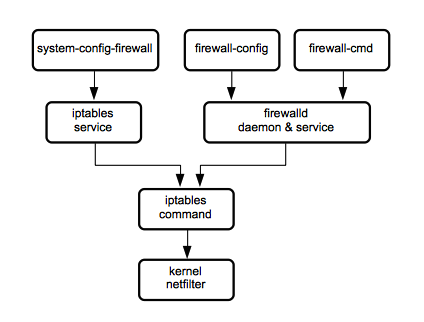
netfilter, iptables tool, iptables service and firewalld
netfilter
netfilter is a set of hooks inside the Linux kernel that allows kernel modules to register callback functions with the network stack. A registered callback function is then called for every packet that traverses the respective hook.
iptables
iptables is a Linux userspace command line tool that manipulates the IPv4 network packet filtering tables and rules. Packet filtering is most commonly used to implement firewalling functionality. It is also used to implement Network Address Translation (NAT). The iptables command is known to yum as "iptables". For more usage details see iptables Command Line Tool.
ip6tables
ip6tables is the equivalent command line tool that manipulates the IPv6 network packet filtering rules. For more usage details, see iptables Command Line Tool.
iptables and ip6tables Services
iptables and ip6tables services are systemd services that use the iptables tool to interact with the kernel netfilter framework. The iptables services are known to yum as "iptables-services". There are two parallel configurations for iptables and ip6tables services.
firewalld
firewalld is a firewall service daemon with D-BUS interface. More details about firewalld available here:
iptables service and firewalld
The iptables service and firewalld are incompatible, you must use one or another.
This is how fiewalld is prevented to start at boot.
Older Firewall Implementations
ipchains
ipfwadm
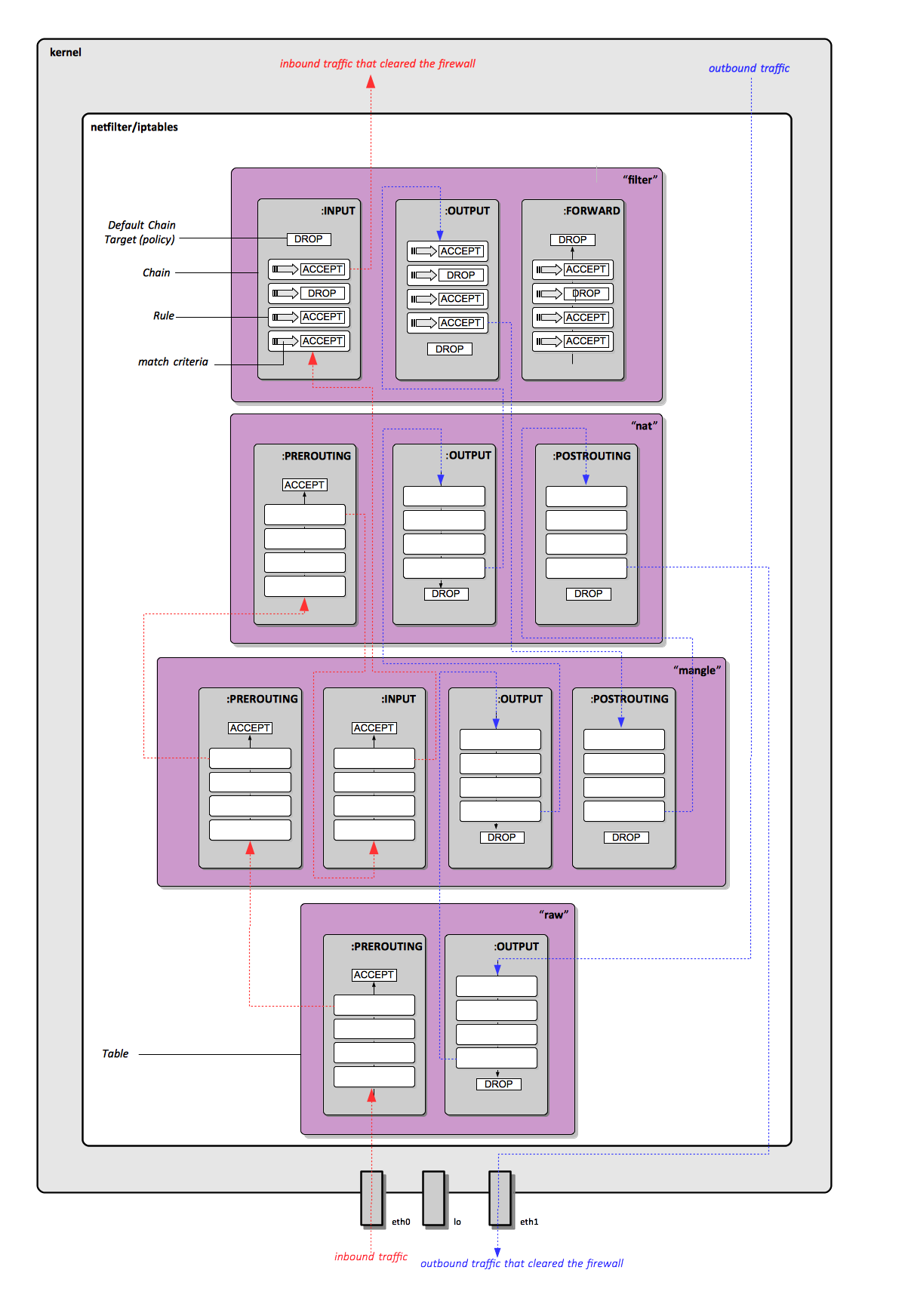
Network Packet Filtering
Every network packet arriving from the network interfaces and every packet originating from applications are passed to iptables, which decides what to do with each one of them. iptables uses the concept of IP addresses, protocols and ports. For a particular packet, only one of the INPUT, OUTPUT or FORWARD chains are used.
Packet Handing Details
iptables State Machine
Table
An iptables table is a data structure that contains a number of built-in chains and may also contain user-defined chains. Several different tables may be defined. Once it is decided a packet is matched against a certain table, the packet is matched against rules contained by that tables' chains. The chains are picked depending on where the packets comes from and the chain semantics. For more details see .
The default table acted upon by the iptables command is "filter". The target table can be changed with -t.
There are currently four independent tables:
!"filter"
The default table; implied when no '-t' option is mentioned. It contains the built-in chains INPUT, FORWARD and OUTPUT.
!"nat"
This table is consulted when a packet that creates a new connection is encountered. It contains the built-in chains PREROUTING, OUTPUT and POSTROUTING.
!"mangle"
This table is used for specialized packet alteration. It contains PREROUTING, OUTPUT, INPUT, FORWARD, POSTROUTING.
- "raw" - This table is used mainly for configuring exemptions from connection tracking in combination with the NOTRACK target. It registers at the netfilter hooks with higher priority and is thus called before ip_conntrack, or any other IP tables. It provides the following built-in chains PREROUTING and OUTPUT.
!Active Tables
Active tables at a certain moment can be queried in:
{{{
/proc/net/ip_tables_names
}}}