AWS CodePipeline Concepts
External
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/latest/userguide/concepts.html
- CreatePipeline API Request Reference
Internal
CodePipeline as AWS Service
CodePipeline is an AWS service, named "codepipeline.amazonaws.com".
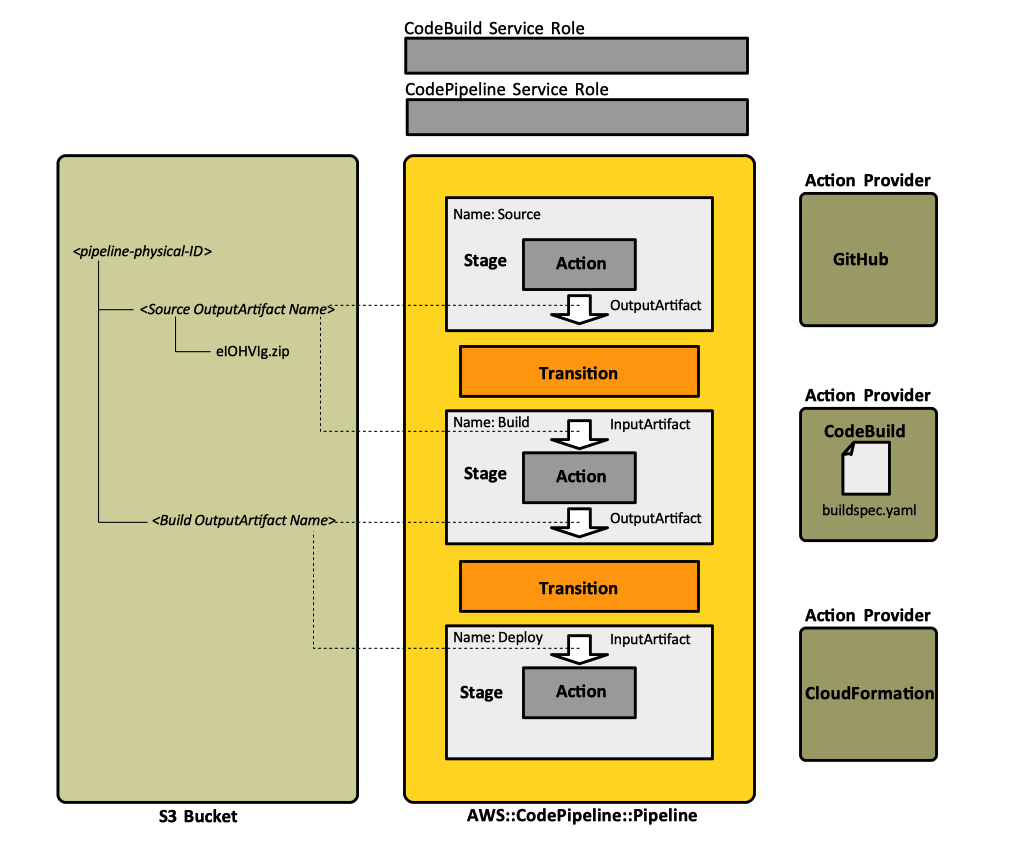
Pipeline
A pipeline is a top-level AWS resource that provides CI/CD release pipeline functionality. It consist in a set of sequential stages, each stage containing one or more actions. A specific stage is always in a fixed position relative to other stages. However, actions within a stage can be executed sequentially, according their run order or in parallel. Stages and actions process artifacts, which "advance" along the pipeline. A pipeline can be created the following CloudFormation sequence:
Resources:
Pipeline:
Name: !Ref AWS::StackName
Type: AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline
Properties:
RoleArn: 'arn:aws:iam::777777777777:role/CodePipelineServiceRole-1'
ArtifactStore
Type: 'S3'
Location: 'experimental-s3-bucket-for-codepipeline'
...
Stages:
...
An example of a simple, working GitHub-based pipeline is available here:
Required Configuration
The pipeline requires a number of configuration properties:
RoleArn
The pipeline needs to be associated with a service role, which allows the codepipeline service to execute various actions required by pipeline operations.
ArtifactStore
The pipeline requires an artifact store, which provides the storage for transient and final artifacts that are processed by the various stages and actions. In most cases, the storage is provided by an Amazon S3 bucket. "Location" specifies the name of the bucket. When the pipeline is initialized, the codepipeline service creates a directory associated with the pipeline. The directory will have the same name as the pipeline. As the pipeline operates, sub-directories corresponding to various input and output artifacts declared by actions will be also created.
Optional Configuration
Optionally, a name can also be configured with a name:
Name
Optional parameter, that provides the physical ID for the pipeline. If not specified, a name will be generated based on the stack-name-Pipeline-24RCYXM52UE6A pattern. A recommended name is:
Name: !Ref AWS::StackName
Stage
A pipeline must have at least 2 stages, one-stage pipeline will be considered invalid. A stage contains one or more actions, which could be executed sequentially or in parallel.
Action
An action is a task performed on an artifact, and it is triggered at a specific stage of a pipeline. The action may occur in a specified order, or in parallel, depending on their configuration. All actions share a common structure:
Action Name
An action name must match the regular expression pattern: [A-Za-z0-9.@\-_]+ The action name must not contain spaces.
Action Type Declaration (ActionTypeId)
The action type declaration specifies an action provider. Currently, six types of actions are supported:
Custom actions can also be developed.
Input Artifacts
An action declares zero or more input artifacts. These are actually files to be processed by the action. As an implementation detail, the name of an input artifact corresponds to the name of a sub-directory of the pipeline directory maintained in the artifact store of the pipeline.
Output Artifacts
An action declares zero or more output artifacts. These are actually files produced by the action. As an implementation detail, the name of an output artifact corresponds to the name of a sub-directory of the pipeline directory maintained in the artifact store of the pipeline.
Run Order
Configuration
Configuration elements are specific to the action provider and are passed to it.
Available Actions
Source
Resources:
MyPipeline:
Type: AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline
Properties:
...
Stages:
- Name: Source
Actions:
- Name: !Sub 'github-pull-${Branch}'
ActionTypeId:
Category: Source
Owner: ThirdParty
Version: '1'
Provider: GitHub
InputArtifacts: []
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: 'sources'
Configuration:
Owner: 'novaordis-llc'
Repo: !Ref GitHubRepositoryName
Branch: !Ref Branch
OAuthToken: '*****'
RunOrder: 1
The action provider, which can be GitHub or other source repository provider, performs a repository clone and packages the content as a ZIP file. The ZIP file is placed in the artifact store, under the directory corresponding to the pipeline and the sub-directory named based on the "OutputArtifacts.Name" configuration element. Assuming that the pipeline is named "thalarion", the output ZIP file is placed in s3://thalarion-buildbucket-enqyf1xp13z2/thalarion/sources.
An example of a simple, working GitHub-based pipeline is available here:
GitHub Authentication
Build
Resources:
MyPipeline:
Type: AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline
Properties:
...
Stages:
...
- Name: Build
Actions:
- Name: !Sub 'CodeBuild-driven-by-${Buildspec}'
ActionTypeId:
Category: Build
Owner: AWS
Version: '1'
Provider: CodeBuild
InputArtifacts:
- Name: 'sources'
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: 'build'
Configuration:
ProjectName: !Ref CodeBuildProject
RunOrder: 1
The action provider, which in this case is the CodeBuild service, executes the build. Existing build projects can be used, or new ones can be created in the CodePipeline console. The build artifacts are placed in the artifact store, under the directory corresponding to the pipeline and the sub-directory named based on the "OutputArtifacts.Name" configuration element. Assuming that the pipeline is named "thalarion", the build artifacts are placed in s3://thalarion-buildbucket-enqyf1xp13z2/thalarion/build-files. The following article explains in detail how CodePipeline and CodeBuild interact:
An example of a simple, working GitHub-based pipeline is available here:
Test
Deploy
Resources:
MyPipeline:
Type: AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline
Properties:
...
Stages:
...
- Name: Deploy
Actions:
- Name: !Sub '${DeploymentStackTemplate}-driven-deployment'
ActionTypeId:
Category: Deploy
Owner: AWS
Version: '1'
Provider: CloudFormation
InputArtifacts:
- Name: 'sources'
- Name: 'build'
OutputArtifacts: []
Configuration:
StackName: !Ref ProjectID
TemplatePath: !Sub sources::${DeploymentStackTemplate}
TemplateConfiguration: build::overrides.json
ParameterOverrides: !Sub '{ "EcrRepository": "${EcrRepository}" }'
ActionMode: CREATE_UPDATE
Capabilities: CAPABILITY_IAM
RoleArn:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub '${ProjectID}-cloudformation-service-role-ARN'
RunOrder: 1
This step relies on the presence of a CloudFormation stack template in the root of the source repository being processed. The name of the template file is configured as "TemplatePath". In the example above, the template path is relative to one of the InputArtifacts. Since that file comes as part of the source tree, we express it relative to the "sources" InputArtifact.
A CloudFront template can be configured externally with parameters, and the deployment template can be configured by providing configuration values in a configuration file, specified as "TemplateConfiguration". "TemplateConfiguration" has the ArtifactName::TemplateConfigurationFileName format, which means that the template configuration file must be produced by one of the previous pipeline steps and must be placed in one of the artifacts. If the template configuration file is not found, maybe because the none of the previous stages created it, the deployment stage will fail with an S3 error. The parameter file allows JSON and YAML.
It is possible to override values in the template configuration file from the pipeline, using the "ParameterOverrides" key. The parameters specified in the "ParameterOverrides" must match with the deployment template (the one specified by TemplatePath) parameters.
An example of a simple, working GitHub-based pipeline is available here:
Approval
Invoke
Custom Action
Custom actions can be developed.