AWS Elastic Load Balancing Concepts
External
Internal
Overview
Load Balancer
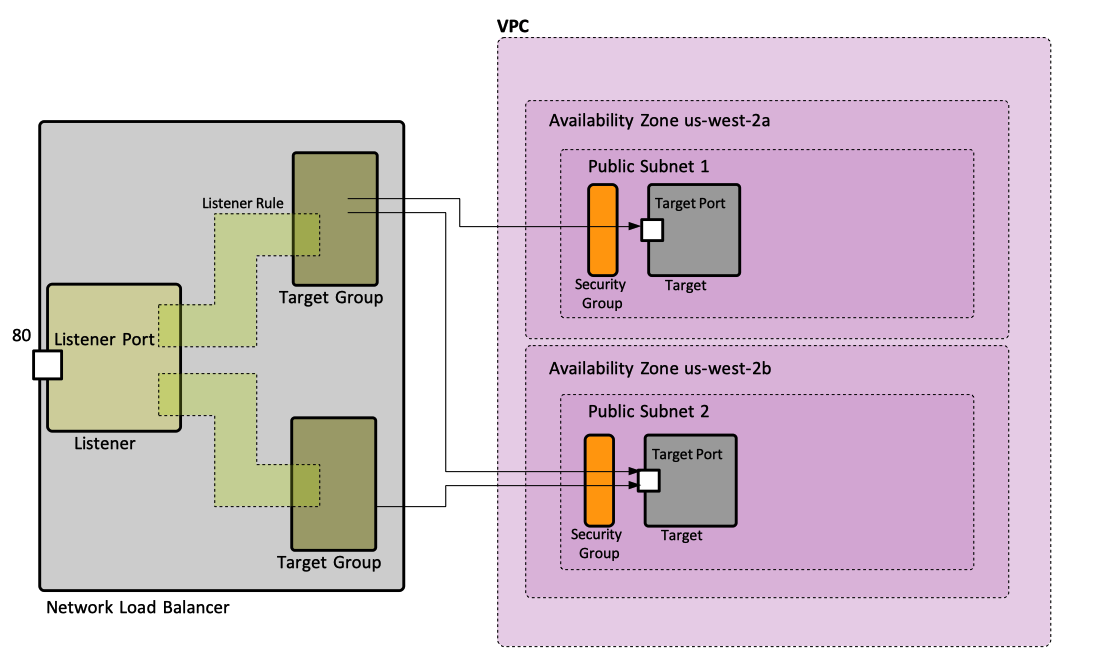
A load balancer serves as the single point of contact for clients, and distributes incoming requests arriving from clients to multiple targets, which actually know how to handle requests and provide responses. The load balancer only knows how to forward requests. This arrangement increases the availability of the application. There are several types of load balancers: application load balancer, network load balancer and classic load balancer. The incoming traffic arrives into the load balancer though one or more listeners, which forward traffic to targets associated with target groups.
Load Balancer Name
The name of a load balancer must be unique within the set of Application Load Balancers and Network Load Balancers for the region. Other documentation section says it must be unique within the AWS account.. I can have a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters and hyphens. A name can't begin with a hyphen. It should not start with "internal-". When creating the load balancer, the name is not required, if missing it will be generated.
Load Balancer Scheme
Internet-Facing
An Internet-facing load balancer routes requests from clients running on the public Internet, to targets.
Internal
An internal load balancer routes requests from clients to targets using private IP addresses.
Load Balancer Types
Used by Amazon ECS.
Application Load Balancer
Allows containers to use dynamic host port mapping (multiple tasks allowed per container instance). Multiple services can use the same listener port on a single load balancer with rule-based routing and paths.
Application Load Balancer Configuration
The following configuration parameters are specific to application load balancers:
- idle_timeout.timeout_seconds: the idle timeout value, in seconds. The valid range is 1-4000 seconds. The default is 60 seconds.
- routing.http2.enabled: indicates whether HTTP/2 is enabled. The value is true or false. The default is true.
Network Load Balancer
A Network Load Balancer functions at the fourth layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. After the load balancer receives a request, it selects a target from the target group for the default rule using a flow hash routing algorithm, based on the protocol, source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port, and TCP sequence number, and then attempts to open a TCP connection to the selected target. It can handle millions of requests per second.
Elastic Load Balancing creates a network interface for each Availability Zone you enable. Each load balancer node in the Availability Zone uses this network interface to get a static IP address. When you create an Internet-facing load balancer, you can optionally associate one Elastic IP address per subnet. Also see Load Balancers and Availability Zones.
Network Load Balancer Configuration
The following configuration parameters are specific to network load balancers:
- load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled indicates whether cross-zone load balancing is enabled. The value is true or false. The default is false.
Network Load Balancer Operations
Classic Load Balancer
Common Load Balancer Configuration
access_logs.s3.enabled
access_logs.s3.bucket
access_logs.s3.prefix
deletion_protection.enabled
Application Load Balancer-Specific Configuration
Network Load Balancer-Specific Configuration
Subnet Mapping
The load balancer can send traffic into one or more subnets, and those are specified in its configuration as either subnets or subnet mappings. For application load balancers, subnets from at lest two availability zones must be specified. Your own Elastic IP addresses cannot be specified.. For network load balancers, subnets from one or more availability zones can be specified. Your own Elastic IP addresses can be specified..
IP Address Type
Represents the type of IP addresses that are used by the load balancer's subnets, such as "ipv4" or "dualstack" (for IPv4 and IPv6 addresses). The default value is 'ipv4'. Only for application load balancers?
Listener
A listener is a process that checks for client connection requests, over a pre-configured protocol and port, and forwards requests to a target group by the means of a load balancer? Rules can be defined for a listener that determine how the load balancer routes requests to the targets in one or more target groups. One listener is defined when the load balancer is created, and more listeners can be added at any time after that.
Listener Protocols
TCP and TLS are available.
Listener Rule
A listener rule is ... and associates a target group with the listener.
Default Listener Rule
There is a default listener rule.
Load Balancer and Availability Zones
The load balancer routes traffic to the targets from availability zones specified in its configuration. All availability zones belong to one VPC, specified in the configuration. Only one subnet per availability zone can be specified. One Elastic IP per availability zone can also be specified, if a specific addresses is required for the load balancer.
Load Balancer Routing
Configuring a load balancer's routing consists in defining target groups, including the ports and protocols associated with those target groups.
Target Group
A target group is ....
A target group can be associated with at most one listener in a load balancer, hence with at most one load balancer. The listener/target group association takes the shape of a listener rule.
There must be at least one target group per load balancer. If just one target group exists, it is the default target group.
A target group routes requests to one or more registered targets, which can be EC2 instances or other types of request-serving endpoints, using a pre-configured TCP protocol and the port. A target can be registered with multiple target groups. A target group supports health checks: health checks are performed on all target registered to a target group that is specified on a listener rule for the load balancer.
Target groups are relevant for AWS CodeDeploy deployments groups, where they are used to route traffic during a deployment.
Target Type
Instance
The target is specified by the instance ID.
IP
The target type is specified by an IP address. The IP address can be specified from one of the following CIDR blocks:
- the subnets of the VPC for the target group.
- 10.0.0.0/8 (RFC 1918)
- 100.64.0.0/10 (RFC 6598)
- 172.16.0.0/12 (RFC 1918)
- 192.168.0.0/16 (RFC 1918)
Publicly routable IP addresses can't be specified.
Target Group Protocol
The protocol the load balancer uses when routing traffic to targets in this target group.
Target Group Port
The port the load balancer uses when routing traffic to targets in this target group.
Target Group Port vs Target Port
Clarify this.
Target
A target is usually an Amazon EC2 instance, but it can also be "serverless" containers launched using FARGATE launch types in ECS clusters.
A target can be registered with multiple target groups.
Target Groups and ECS FARGATE Targets
A target group to send traffic into ECS FARGATE targets should be of type "ip". The target group should be available when the ECS service is created, and the targets are correctly registered even if they get dynamic IP addresses. More than that, if the ECS task is stopped, the target group adjusts automatically:
After a while:
Health Checks
Health checks are configured on a per-target group basis. A health check configured on a target group is performed on all targets registered with that target group.